Rapid Discrimination of Panax quinquefolium and Panax ginseng Using the Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Technique
- PMID: 37836715
- PMCID: PMC10574230
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28196872
Rapid Discrimination of Panax quinquefolium and Panax ginseng Using the Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Technique
Abstract
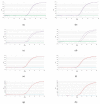
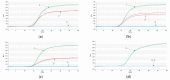
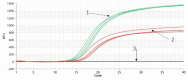
This study aims to establish a rapid identification method based on the Proofman-LMTIA technique for distinguishing between Panax quinquefolium and Panax ginseng. By targeting specific 18S rDNA sequences, suitable primers and Proofman probes labeled FAM or JOE were designed for LMTIA. Initially, single-species-primer Proofman-LMTIA assays were performed separately for each ginseng type to optimize reaction temperature, assess sensitivity and specificity, and determine the detection limit. Subsequently, both sets of primers and their corresponding probes were combined in the same reaction system to further optimize reaction conditions, evaluate sensitivity, and assess stability. Finally, the developed Proofman-duplex-LMTIA technique was employed to detect P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng slices available in the market. Single-plex Proofman-LMTIA assays revealed that the optimal reaction temperature for both P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng was 62 °C. The sensitivity was as low as 1 pg/μL, with a detection limit of 0.1%, and both showed excellent specificity. The optimal temperature for Proofman-duplex-LMTIA assays was 58 °C. This method could simultaneously identify P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng. Testing 6 samples of P. ginseng and 11 samples of P. quinquefolium from the market resulted in a 100% positive rate for all samples. This study successfully established a rapid, simple, sensitive, and specific Proofman-duplex-LMTIA identification method for P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng. It provides an effective means for quality control of P. quinquefolium, P. ginseng, and related products.
Keywords: Panax ginseng; Panax quinquefolium; Proofman probe; ladder melting temperature isothermal amplification; rapid identification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee . Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Volume 1. China Medical Science and Technology Press; Beijing, China: 2020. (In Chinese)
-
- Tian X., Lv S., Tian H., Wang R., Wang H. Development of an accurate and reliable DNA method for botanical origin authentication of ginseng food products. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2020;87:103419. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103419. - DOI
-
- Lin F., Cao H., Ren H., Yao L. Seeds identification of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium using ITS2 DNA barcordes. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2019;50:2188–2193. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.09.026. (In Chinese) - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

