Heterointerface Engineered Core-Shell Fe2O3@TiO2 for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Storage
- PMID: 37836746
- PMCID: PMC10574312
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28196903
Heterointerface Engineered Core-Shell Fe2O3@TiO2 for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Storage
Abstract
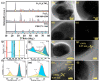
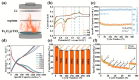
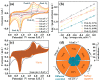
The rational design of the heterogeneous interfaces enables precise adjustment of the electronic structure and optimization of the kinetics for electron/ion migration in energy storage materials. In this work, the built-in electric field is introduced to the iron-based anode material (Fe2O3@TiO2) through the well-designed heterostructure. This model serves as an ideal platform for comprehending the atomic-level optimization of electron transfer in advanced lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). As a result, the core-shell Fe2O3@TiO2 delivers a remarkable discharge capacity of 1342 mAh g-1 and an extraordinary capacity retention of 82.7% at 0.1 A g-1 after 300 cycles. Fe2O3@TiO2 shows an excellent rate performance from 0.1 A g-1 to 4.0 A g-1. Further, the discharge capacity of Fe2O3@TiO2 reached 736 mAh g-1 at 1.0 A g-1 after 2000 cycles, and the corresponding capacity retention is 83.62%. The heterostructure forms a conventional p-n junction, successfully constructing the built-in electric field and lithium-ion reservoir. The kinetic analysis demonstrates that Fe2O3@TiO2 displays high pseudocapacitance behavior (77.8%) and fast lithium-ion reaction kinetics. The capability of heterointerface engineering to optimize electrochemical reaction kinetics offers novel insights for constructing high-performance iron-based anodes for LIBs.
Keywords: built-in electric field; electrochemical kinetics; heterointerface engineering; iron-based anode; lithium-ion storage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sun C., Chen F., Tang X., Zhang D., Zheng K., Zhu G., Bin Shahid U., Liu Z., Shao M., Wang J. Simultaneous interfacial interaction and built-in electric field regulation of GaZnON@NG for high-performance lithium-ion storage. Nano Energy. 2022;99:107369. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107369. - DOI
-
- Zhao L., Ning Y., Dong Q., Ullah Z., Zhu P., Zheng S., Xia G., Zhu S., Li Q., Liu L. Longer cycle life and higher discharge voltage of a small molecular indanthrone resulting from the extended conjugated framework. J. Power Sources. 2023;556:232518. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.232518. - DOI
-
- Mostafa M.M.M., Alshehri A.A., Salama R.S. High performance of supercapacitor based on alumina nanoparticles derived from Coca-Cola cans. J. Energy Storage. 2023;64:107168. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.107168. - DOI
-
- Yan Z., Li J., Chen Q., Chen S., Luo L., Chen Y. Synthesis of CoSe2/Mxene Composites Using as High-performance Anode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022;5:2977–2987. doi: 10.1007/s42114-022-00524-0. - DOI
-
- Zhu Y., Zhang Y., Das P., Wu Z.-S. Recent Advances in Interface Engineering and Architecture Design of Air-Stable and Water-Resistant Lithium Metal Anodes. Energy Fuels. 2021;35:12902–12920. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c01904. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2023M733754/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 52072196/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZR2023QE059/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- 2020A1515111086/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 2020A1515110219/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

