Comparative Analysis of Predictive Interstitial Glucose Level Classification Models
- PMID: 37837098
- PMCID: PMC10574913
- DOI: 10.3390/s23198269
Comparative Analysis of Predictive Interstitial Glucose Level Classification Models
Abstract
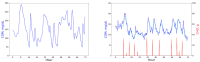
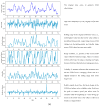
Background: New methods of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) provide real-time alerts for hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, and rapid fluctuations of glucose levels, thereby improving glycemic control, which is especially crucial during meals and physical activity. However, complex CGM systems pose challenges for individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals, particularly when interpreting rapid glucose level changes, dealing with sensor delays (approximately a 10 min difference between interstitial and plasma glucose readings), and addressing potential malfunctions. The development of advanced predictive glucose level classification models becomes imperative for optimizing insulin dosing and managing daily activities.
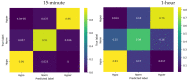
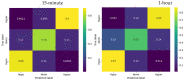
Methods: The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of three different predictive models for the glucose level classification: (1) an autoregressive integrated moving average model (ARIMA), (2) logistic regression, and (3) long short-term memory networks (LSTM). The performance of these models was evaluated in predicting hypoglycemia (<70 mg/dL), euglycemia (70-180 mg/dL), and hyperglycemia (>180 mg/dL) classes 15 min and 1 h ahead. More specifically, the confusion matrices were obtained and metrics such as precision, recall, and accuracy were computed for each model at each predictive horizon.
Results: As expected, ARIMA underperformed the other models in predicting hyper- and hypoglycemia classes for both the 15 min and 1 h horizons. For the 15 min forecast horizon, the performance of logistic regression was the highest of all the models for all glycemia classes, with recall rates of 96% for hyper, 91% for norm, and 98% for hypoglycemia. For the 1 h forecast horizon, the LSTM model turned out to be the best for hyper- and hypoglycemia classes, achieving recall values of 85% and 87% respectively.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that different models may have varying strengths and weaknesses in predicting glucose level classes, and the choice of model should be carefully considered based on the specific requirements and context of the clinical application. The logistic regression model proved to be more accurate for the next 15 min, particularly in predicting hypoglycemia. However, the LSTM model outperformed logistic regression in predicting glucose level class for the next hour. Future research could explore hybrid models or ensemble approaches that combine the strengths of multiple models to further enhance the accuracy and reliability of glucose predictions.
Keywords: ARIMA; CGM; LSTM; diabetes; hyperglycemia; hypoglycemia; logistic regression; prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reliability of Inpatient CGM: Comparison to Standard of Care.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023 Mar;17(2):329-335. doi: 10.1177/19322968211062168. Epub 2021 Dec 15. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 34911384 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing sensor accuracy for non-adjunct use of continuous glucose monitoring.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015 Mar;17(3):177-86. doi: 10.1089/dia.2014.0272. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25436913 Free PMC article.
-
Forecasting of Glucose Levels and Hypoglycemic Events: Head-to-Head Comparison of Linear and Nonlinear Data-Driven Algorithms Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Only.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 27;21(5):1647. doi: 10.3390/s21051647. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673415 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Glucose Monitoring, Future Products, and Update on Worldwide Artificial Pancreas Projects.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016 Feb;18 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S253-63. doi: 10.1089/dia.2015.0345. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26784131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review Supporting the Endocrine Society Guidelines: Management of Diabetes and High Risk of Hypoglycemia.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Feb 15;108(3):592-603. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac601. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36477885
Cited by
-
Optimizing type 2 diabetes management: AI-enhanced time series analysis of continuous glucose monitoring data for personalized dietary intervention.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Apr 22;10:e1971. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1971. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 38686006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zaharieva D.P., Turksoy K., McGaugh S.M., Pooni R., Vienneau T., Ly T., Riddell M.C. Lag Time Remains with Newer Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Technology During Aerobic Exercise in Adults Living with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019;21:313–321. doi: 10.1089/dia.2018.0364. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

