Inhibitory effect and mechanism of Rosiglitazone on M1 type polarization of central microglia in intracerebral hemorrhage mice based on JNK/STAT3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 37837628
- PMCID: PMC10726784
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.3275
Inhibitory effect and mechanism of Rosiglitazone on M1 type polarization of central microglia in intracerebral hemorrhage mice based on JNK/STAT3 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) seriously threatens the health of people. In addition, microglia M1 polarization was confirmed to be involved in the progression of ICH. Rosiglitazone was able to be used as an antidiabetic agent, which could activate PPAR-γ, and PPAR-γ was reported to inhibit inflammation in microglia. However, the detailed function of Rosiglitazone in ICH remains unclear.
Methods: In vivo and in vitro experiments were used to test the function of Rosiglitazone in ICH. In addition, RT-qPCR and western blot were performed to evaluate the mRNA and protein level of PPAR-γ, respectively. Immunofluorescence staining was performed to detect the levels of CD206 and CD86, and ELISA was used to measure the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
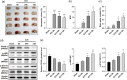
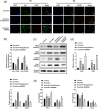
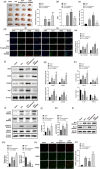
Results: PPAR-γ was downregulated in ICH mice, whereas p-JNK and p-STAT3 were upregulated. Thrombin notably downregulated the level of PPAR-γ in BV2 cells, whereas Rosiglitazone partially reversed this phenomenon. In addition, Rosiglitazone markedly reversed thrombin-induced microglia M1 polarization. Consistently, thrombin-induced inflammatory response in BV2 cells was abolished in the presence of Rosiglitazone. SP600125 (JNK/STAT3 inhibitor) greatly reversed thrombin-induced M1 polarization in microglia, and GW9662 abolished the effect of SP600125. Meanwhile, Rosiglitazone could inactivate JNK/STAT3 pathway through the upregulation of PPAR-γ. Furthermore, Rosiglitazone notably alleviated the symptom of ICH in vivo through inhibiting the apoptosis and mediating PPAR-γ/JNK/STAT3 axis.
Conclusion: Rosiglitazone could attenuate the inflammation in ICH through inhibiting microglia M1 polarization. Thus, our research would shed now lights on exploring new therapeutic strategies against ICH.
Keywords: JNK/STAT3; PPAR-γ; Rosiglitazone; intracerebral hemorrhage.
© 2023 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
These authors declared no conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures


References
-
- Cheng, W.‐L. , Zhang, Q. , Li, Bo. , Cao, J.‐L. , Jiao, L. , Chao, S.‐P. , Lu, Z. , & Zhao, F. (2021). PAK1 silencing attenuated proinflammatory macrophage activation and foam cell formation by increasing PPAR‐gamma expression. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 6957900. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dicpinigaitis, A J. , Feldstein, E. , Shapiro, S D. , Kamal, H. , Bauerschmidt, A. , Rosenberg, J. , Amuluru, K. , Pisapia, J. , Dangayach, N S. , Liang, J W. , Bowers, C A. , Mayer, S A. , Gandhi, C D. , & Al‐Mufti, F. (2022). Cerebral vasospasm following arteriovenous malformation rupture: A population‐based cross‐sectional study. Neurosurgical Focus, [Electronic Resource], 53(1), E15. - PubMed
-
- Duan, S. , Wang, F. , Cao, J. , & Wang, C. (2020). Exosomes derived from microRNA‐146a‐5p‐enriched bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and microglial M1 polarization. Drug Designs Development and Therapiae, 14, 3143–3158. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

