dcSBM: A federated constrained source-based morphometry approach for multivariate brain structure mapping
- PMID: 37837630
- PMCID: PMC10619413
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.26483
dcSBM: A federated constrained source-based morphometry approach for multivariate brain structure mapping
Abstract
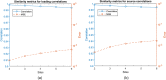
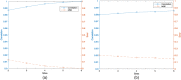
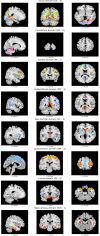
The examination of multivariate brain morphometry patterns has gained attention in recent years, especially for their powerful exploratory capabilities in the study of differences between patients and controls. Among the many existing methods and tools for the analysis of brain anatomy based on structural magnetic resonance imaging data, data-driven source-based morphometry (SBM) focuses on the exploratory detection of such patterns. Here, we implement a semi-blind extension of SBM, called constrained source-based morphometry (constrained SBM), which enables the extraction of maximally independent reference-alike sources using the constrained independent component analysis (ICA) approach. To do this, we combine SBM with a set of reference components covering the full brain, derived from a large independent data set (UKBiobank), to provide a fully automated SBM framework. This also allows us to implement a federated version of constrained SBM (cSBM) to allow analysis of data that is not locally accessible. In our proposed decentralized constrained source-based morphometry (dcSBM), the original data never leaves the local site. Each site operates constrained ICA on its private local data using a common distributed computation platform. Next, an aggregator/master node aggregates the results estimated from each local site and applies statistical analysis to estimate the significance of the sources. Finally, we utilize two additional multisite patient data sets to validate our model by comparing the resulting group difference estimates from both cSBM and dcSBM.
Keywords: SBM; federated learning; neuroimaging; sMRI.
© 2023 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

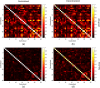
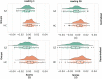

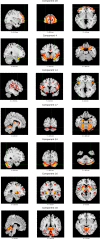

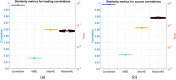
References
-
- Abrol, A. , Fu, Z. , Du, Y. , & Calhoun, V. D. (2019). Multimodal data fusion of deep learning and dynamic functional connectivity features to predict Alzheimer's disease progression. In 2019 41st annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC) (pp. 4409–4413). IEEE. - PubMed
-
- Aine, C. , Bockholt, H. J. , Bustillo, J. R. , Cañive, J. M. , Caprihan, A. , Gasparovic, C. , Hanlon, F. M. , Houck, J. M. , Jung, R. E. , Lauriello, J. , Liu, J. , Mayer, A. R. , Perrone‐Bizzozero, N. I. , Posse, S. , Stephen, J. M. , Turner, J. A. , Clark, V. P. , & Calhoun, V. D. (2017). Multimodal neuroimaging in schizophrenia: Description and dissemination. Neuroinformatics, 15(4), 343–364. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bostami, B. , Calhoun, V. D. , Van Der Horn, H. J. , & Vergara, V. (2021). Harmonization of multi‐site dynamic functional connectivity network data. In 2021 IEEE 21st international conference on bioinformatics and bioengineering (BIBE) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

