A Circulating Panel of circRNA Biomarkers for the Noninvasive and Early Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37839499
- PMCID: PMC10843014
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.050
A Circulating Panel of circRNA Biomarkers for the Noninvasive and Early Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background & aims: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most fatal malignancies. Delayed manifestation of symptoms and lack of specific diagnostic markers lead patients being diagnosed with PDAC at advanced stages. This study aimed to develop a circular RNA (circRNA)-based biomarker panel to facilitate noninvasive and early detection of PDAC.
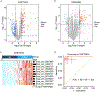
Methods: A systematic genome-wide discovery of circRNAs overexpressed in patients with PDAC was conducted. Subsequently, validation of the candidate markers in the primary tumors from patients with PDAC was performed, followed by their translation into a plasma-based liquid biopsy assay by analyzing 2 independent clinical cohorts of patients with PDAC and nondisease controls. The performance of the circRNA panel was assessed in conjunction with the plasma levels of cancer antigen 19-9 for the early detection of PDAC.
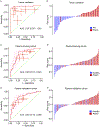
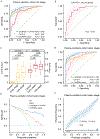
Results: Initially, a panel of 10 circRNA candidates was identified during the discovery phase. Subsequently, the panel was reduced to 5 circRNAs in the liquid biopsy-based assay, which robustly identified patients with PDAC and distinguished between early-stage (stage I/II) and late-stage (stage III/IV) disease. The areas under the curve of this diagnostic panel for the detection of early-stage PDAC were 0.83 and 0.81 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. Moreover, when this panel was combined with cancer antigen 19-9 levels, the diagnostic performance for identifying patients with PDAC improved remarkably (area under the curve, 0.94) for patients in the validation cohort. Furthermore, the circRNA panel could also efficiently identify patients with PDAC (area under the curve, 0.85) who were otherwise deemed clinically cancer antigen 19-9-negative (<37 U/mL).
Conclusions: A circRNA-based biomarker panel with a robust noninvasive diagnostic potential for identifying patients with early-stage PDAC was developed.
Keywords: CA19-9; Circular RNA; Diagnostic Biomarker; Liquid-Biopsy Assay; Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2024 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 2022, 72(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Versteijne E, van Dam JL, Suker M, Janssen QP, Groothuis K, Akkermans-Vogelaar JM, Besselink MG, Bonsing BA, Buijsen J, Busch OR et al.: Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Versus Upfront Surgery for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: Long-Term Results of the Dutch Randomized PREOPANC Trial. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40(11):1220–1230. - PubMed
-
- Toft J, Hadden WJ, Laurence JM, Lam V, Yuen L, Janssen A, Pleass H: Imaging modalities in the diagnosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic accuracy. Eur J Radiol 2017, 92:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Scara S, Bottoni P, Scatena R: CA 19–9: Biochemical and Clinical Aspects. Adv Exp Med Biol 2015, 867:247–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

