Activity of novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations against serine carbapenemase-producing carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 37840005
- PMCID: PMC10689909
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkad225
Activity of novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations against serine carbapenemase-producing carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is complex and multifaceted. While the novel β-lactamase inhibitors (BLIs) avibactam, relebactam and vaborbactam inhibit serine-based β-lactamases, the comparative potency of the novel β-lactam (BL)/BLI combinations against serine carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa is unknown.
Objectives: To compare the in vitro activity of ceftazidime/avibactam, ceftazidime, imipenem/relebactam, imipenem, meropenem/vaborbactam and meropenem against serine β-lactamase-producing P. aeruginosa.
Methods: Carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa were collated through the Enhancing Rational Antimicrobials against Carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa (ERACE-PA) Global Surveillance. Isolates positive for serine-based carbapenemases were assessed. MICs were determined by broth microdilution to each novel BL/BLI and BL alone.
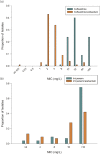
Results: GES was the most common carbapenemase identified (n = 59) followed by KPC (n = 8). Ceftazidime/avibactam had MIC50/MIC90 values of 4/8 mg/L and 91% of isolates were susceptible. Conversely, ceftazidime alone was active against only 3% of isolates. The MIC50/MIC90 of imipenem/relebactam were 16/>16 mg/L and 13% of all isolates were defined as susceptible. Of the KPC-producing isolates, 38% were susceptible to imipenem/relebactam, compared with 0% to imipenem. The meropenem/vaborbactam MIC50/MIC90 were >16/>16 mg/L, and 6% of isolates were susceptible, which was similar to meropenem alone (MIC50/90, >8/>8 mg/L; 3% susceptible) suggesting the addition of vaborbactam cannot overcome co-expressed, non-enzymatic resistance mechanisms.
Conclusions: Among the novel BL/BLIs, ceftazidime/avibactam displayed better in vitro activity and thus is a rational treatment option for serine carbapenemase-harbouring P. aeruginosa. While imipenem/relebactam displayed some activity, particularly against isolates with blaKPC, meropenem/vaborbactam exhibited poor activity, with MICs similar to meropenem alone.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures

References
-
- Weiner LM, Webb AK, Limbago B et al. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers For Disease Control and Prevention, 2011–2014. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2016; 37: 1288–301. 10.1017/ice.2016.174 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- CDC . Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States 2019. 2019.. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/threats-report/2019-ar-threats-re....

