Lung inflammation and interstitial fibrosis by targeted alveolar epithelial type I cell death
- PMID: 37841243
- PMCID: PMC10568624
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1261483
Lung inflammation and interstitial fibrosis by targeted alveolar epithelial type I cell death
Abstract
Introduction: The pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases is multifaceted with a major role of recurrent micro-injuries of the epithelium. While several reports clearly indicated a prominent role for surfactant-producing alveolar epithelial type 2 (AT2) cells, the contribution of gas exchange-permissive alveolar epithelial type 1 (AT1) cells has not been addressed yet. Here, we investigated whether repeated injury of AT1 cells leads to inflammation and interstitial fibrosis.
Methods: We chose an inducible model of AT1 cell depletion following local diphtheria toxin (DT) administration using an iDTR flox/flox (idTRfl/fl) X Aquaporin 5CRE (Aqp5CRE) transgenic mouse strain.
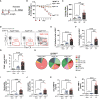
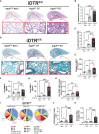
Results: We investigated repeated doses and intervals of DT to induce cell death of AT1 cells causing inflammation and interstitial fibrosis. We found that repeated DT administrations at 1ng in iDTRfl/fl X Aqp5CRE mice cause AT1 cell death leading to inflammation, increased tissue repair markers and interstitial pulmonary fibrosis.
Discussion: Together, we demonstrate that depletion of AT1 cells using repeated injury represents a novel approach to investigate chronic lung inflammatory diseases and to identify new therapeutic targets.
Keywords: AT1 cell depletion; cell death; iDTR; lung injury; sterile inflammation.
Copyright © 2023 Carignon, De Moura Rodrigues, Gosset, Culerier, Huot-Marchand, Savigny, Kaya, Quesniaux, Gombault, Couillin, Ryffel, Le Bert and Riteau.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

