Conditional activation of an anti-IgM antibody-drug conjugate for precise B cell lymphoma targeting
- PMID: 37841262
- PMCID: PMC10569071
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1258700
Conditional activation of an anti-IgM antibody-drug conjugate for precise B cell lymphoma targeting
Abstract
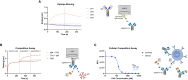
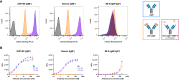
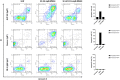
Cancerous B cells are almost indistinguishable from their non-malignant counterparts regarding their surface antigen expression. Accordingly, the challenge to be faced consists in elimination of the malignant B cell population while maintaining a functional adaptive immune system. Here, we present an IgM-specific antibody-drug conjugate masked by fusion of the epitope-bearing IgM constant domain. Antibody masking impaired interaction with soluble pentameric as well as cell surface-expressed IgM molecules rendering the antibody cytotoxically inactive. Binding capacity of the anti-IgM antibody drug conjugate was restored upon conditional protease-mediated demasking which consequently enabled target-dependent antibody internalization and subsequent induction of apoptosis in malignant B cells. This easily adaptable approach potentially provides a novel mechanism of clonal B cell lymphoma eradication to the arsenal available for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma treatment.
Keywords: B cell lymphoma; B cell receptor; MMP-9; antibody-drug conjugate; conditional activated antibody; masked antibody; matriptase.
Copyright © 2023 Schoenfeld, Harwardt, Habermann, Elter and Kolmar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


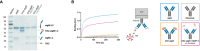

Similar articles
-
Specific Targeting of Lymphoma Cells Using Semisynthetic Anti-Idiotype Shark Antibodies.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 26;11:560244. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.560244. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33324393 Free PMC article.
-
AGS67E, an Anti-CD37 Monomethyl Auristatin E Antibody-Drug Conjugate as a Potential Therapeutic for B/T-Cell Malignancies and AML: A New Role for CD37 in AML.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Jul;14(7):1650-60. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0067. Epub 2015 May 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25934707 Free PMC article.
-
DCDT2980S, an anti-CD22-monomethyl auristatin E antibody-drug conjugate, is a potential treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Jul;12(7):1255-65. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1173. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23598530
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
SAR3419: an anti-CD19-Maytansinoid Immunoconjugate for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Oct 15;17(20):6448-58. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0485. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22003072 Review.
Cited by
-
A Conditionally Activated Cytosol-Penetrating Antibody for TME-Dependent Intracellular Cargo Delivery.Antibodies (Basel). 2024 May 2;13(2):37. doi: 10.3390/antib13020037. Antibodies (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38804305 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Stimulation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells with CpG ODN2006 and α-IgM Antibodies Leads to Strong Immune Responses in Monocytes Independent of B Cell Activation.Cells. 2024 Nov 5;13(22):1822. doi: 10.3390/cells13221822. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594572 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Therapeutic Antibodies for Cancer Treatment: Advancements, Applications, and Challenges.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 2. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01270-y. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39222285 Review.
-
T cell receptor-directed antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of T cell-derived cancers.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Jul 19;32(3):200850. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200850. eCollection 2024 Sep 19. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39176070 Free PMC article.
-
Bispecific killer cell engagers employing species cross-reactive NKG2D binders redirect human and murine lymphocytes to ErbB2/HER2-positive malignancies.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1457887. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1457887. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39267747 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

