A comprehensive characterization of longevity and culling reasons in Canadian Holstein cattle based on various systematic factors
- PMID: 37841322
- PMCID: PMC10576516
- DOI: 10.1093/tas/txad102
A comprehensive characterization of longevity and culling reasons in Canadian Holstein cattle based on various systematic factors
Abstract
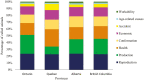
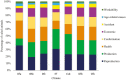
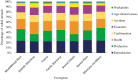
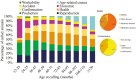
The decision of premature culling cows directly impacts the profitability of dairy farms. A comprehensive characterization of the primary causes of culling reasons would greatly improve both management and selection objectives in dairy cattle breeding programs. Therefore, this study aimed to analyze the temporal frequencies of 34 culling reasons in Canadian Holstein cows. After data editing and quality control, records from 3,096,872 cows culled from 9,683 herds spread across Canada were used for the analyses covering the periods from 1996 to 2020. Reproductive issues were the main culling reason accounting for 23.02%, followed by milk production (20.82%), health (20.39%), conformation problems (13.69%), economic factors (13.10%), accidents (5.67%), age-related causes (1.67%), and workability (1.63%). Nearly fifty-eight percent of cows were culled after 47 months of age. The observed frequencies of culling due to economic factors were lower than expected from 1996 to 2014 and higher than expected between 2015 and 2020. Reproduction issues had the highest culling frequencies during fall (24.54%), winter (24.02%), and spring (22.51%), while health issues were the most frequent (22.51%) culling reason in the summer season. Health issues (25.50%) and milk production (27.71%) were the most frequent culling reasons in the provinces of Quebec and Ontario, respectively. Reproductive issues showed the highest frequency across climates based on the Köppen climate classification, except for Csb (Dry-summer subtropical or Mediterranean climate) and Bsk (Middle latitude steppe climate), which correspond to small regions in Canada, where production was the most frequent culling reason (29.42% and 21.56%, respectively). Reproductive and milk performance issues were the two main culling reasons in most ecozones, except in Boreal Shield and Atlantic Marine, where health issues had the highest frequencies (25.12 and 23.75%, respectively). These results will contribute to improving management practices and selective decisions to reduce involuntary culling of Holstein cows.
Keywords: dairy cow; durability; herd replacement; productive life; reproductive failure; stayability.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society of Animal Science.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Associations between the breeding values of Holstein-Friesian bulls and longevity and culling reasons of their daughters.Animal. 2021 May;15(5):100204. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2021.100204. Epub 2021 May 23. Animal. 2021. PMID: 34029794
-
Management of heat stress to improve fertility in dairy cows in Israel.J Reprod Dev. 2010 Jan;56 Suppl:S36-41. doi: 10.1262/jrd.1056s36. J Reprod Dev. 2010. PMID: 20629215
-
Effects of extending dairy cow longevity by adjusted reproduction management decisions on partial net return and greenhouse gas emissions: A dynamic stochastic herd simulation study.J Dairy Sci. 2024 Sep;107(9):6902-6912. doi: 10.3168/jds.2023-24089. Epub 2024 Apr 25. J Dairy Sci. 2024. PMID: 38670339
-
Symposium review: Why revisit dairy cattle productive lifespan?J Dairy Sci. 2020 Apr;103(4):3838-3845. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17361. Epub 2020 Feb 20. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 32089299 Review.
-
Symposium review: An abundance of replacement heifers: What is the economic impact of raising more than are needed?J Dairy Sci. 2020 Apr;103(4):3828-3837. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17143. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 32037180 Review.
Cited by
-
Longevity and Culling Reasons in Dairy Herds in Southern Brazil.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 29;15(15):2232. doi: 10.3390/ani15152232. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805022 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing age-related features for assessing biological age and characteristics in Xinjiang Brown cattle.BMC Genomics. 2025 May 29;26(1):542. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11430-2. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40442598 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association and functional annotation analyses reveal candidate genes and pathways associated with various ewe longevity indicators in U.S. Katahdin sheep.Front Genet. 2025 Jul 3;16:1600587. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1600587. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40678382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdisa, T. 2018. Review on the reproductive health problem of dairy cattle. J. Dairy and Vet. Sci. 5:555655. doi: 10.19080/jdvs.2018.05.555655 - DOI
-
- Adamczyk, K., Jagusiak W., and Makulska J... 2018. Analysis of lifetime performance and culling reasons in black-and-white holstein-friesian cows compared with crossbreds. Ann. Anim. Sci. 18:1061–1079. doi: 10.2478/AOAS-2018-0036 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
