Mass spectrometry-based analysis of gut microbial metabolites of aromatic amino acids
- PMID: 37841334
- PMCID: PMC10570628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.09.032
Mass spectrometry-based analysis of gut microbial metabolites of aromatic amino acids
Abstract
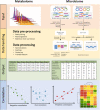
Small molecules derived from gut microbiota have been increasingly investigated to better understand the functional roles of the human gut microbiome. Microbial metabolites of aromatic amino acids (AAA) have been linked to many diseases, such as metabolic disorders, chronic kidney diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, and cancer. Important microbial AAA metabolites are often discovered via global metabolite profiling of biological specimens collected from humans or animal models. Subsequent metabolite identity confirmation and absolute quantification using targeted analysis enable comparisons across different studies, which can lead to the establishment of threshold concentrations of potential metabolite biomarkers. Owing to their excellent selectivity and sensitivity, hyphenated mass spectrometry (MS) techniques are often employed to identify and quantify AAA metabolites in various biological matrices. Here, we summarize the developments over the past five years in MS-based methodology for analyzing gut microbiota-derived AAA. Sample preparation, method validation, analytical performance, and statistical methods for correlation analysis are discussed, along with future perspectives.
Keywords: Aromatic amino acid; Gut microbial metabolite; Mass spectrometry; Metabolomics; Quantitative analysis.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metabolome analysis for investigating host-gut microbiota interactions.J Formos Med Assoc. 2019 Mar;118 Suppl 1:S10-S22. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Formos Med Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30269936 Review.
-
Challenges of metabolomics in human gut microbiota research.Int J Med Microbiol. 2016 Aug;306(5):266-279. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Int J Med Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27012595 Review.
-
Key bacterial taxa determine longitudinal dynamics of aromatic amino acid catabolism in infants' gut.Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2221426. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2221426. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 37357437 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbial metabolome in inflammatory bowel disease: From association to therapeutic perspectives.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Apr 4;20:2402-2414. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.03.038. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35664229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Development of a widely-targeted metabolomics method based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2023 Jun 8;41(6):520-526. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.10003. Se Pu. 2023. PMID: 37259877 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Microbiota Metabolite Profiles and Dietary Intake in Older Individuals with Insomnia of Short vs. Normal Sleep Duration.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 30;14(4):419. doi: 10.3390/biom14040419. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672436 Free PMC article.
-
Using metabolomics to investigate the relationship between the metabolomic profile of the intestinal microbiota derivatives and mental disorders in inflammatory bowel diseases: a narrative review.Res Pharm Sci. 2025 Feb 20;20(1):1-24. doi: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_273_23. eCollection 2025 Feb. Res Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40190827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Data processing solutions to render metabolomics more quantitative: case studies in food and clinical metabolomics using Metabox 2.0.Gigascience. 2024 Jan 2;13:giae005. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giae005. Gigascience. 2024. PMID: 38488666 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Phenolic Acids Produced from Food-Derived Flavonoids and Amino Acids by the Gut Microbiota on Health and Disease.Molecules. 2024 Oct 29;29(21):5102. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215102. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCarville J.L., Chen G.Y., Cuevas V.D., et al. Microbiota metabolites in health and disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 2020;38:147–170. - PubMed
-
- Fan Y., Pedersen O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:55–71. - PubMed
-
- Wishart D.S. Metabolomics for investigating physiological and pathophysiological processes. Physiol Rev. 2019;99:1819–1875. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
