Expression of CKS2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Correlation with Survival Outcomes and Immune Microenvironment
- PMID: 37841370
- PMCID: PMC10572409
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S427624
Expression of CKS2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Correlation with Survival Outcomes and Immune Microenvironment
Abstract
Purpose: Cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit 2 (CKS2) has an important function in regulating cancer progression and cell cycle. This research aims to ascertain how CKS2 plays its part through multi-omics analyses, to reveal its relationship with the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Material and methods: Multiple databases were used to determine the transcriptional data of CKS2, epigenetic changes, and effects thereof upon the prognosis of HCC patients. The biological functions of CKS2 in HCC were expounded by functional enrichment analysis. TIMER, GSEA, TIP, and online single-cell sequencing databases were adopted for revealing correlations of CKS2 expression with infiltration of immune cells, immunomodulators, immunity cycle, and immune markers in the immune microenvironment of HCC. In addition, qRT-PCR and Western blot were used to validate gene expression in tissues from HCC patients.
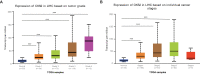
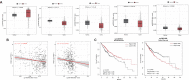
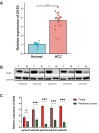
Results: Open database analysis confirmed that CKS2 is highly expressed in HCC and that it is related to poor prognosis in HCC patients. Aberrant methylation levels of the two methylation sites of CKS2 in HCC contributed to its high expression and were correlated significantly with survival. The CKS2 expression was positively correlated with most immunomodulators and infiltration levels for B and CD8+T cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages, especially exhausted CD8+T cells. Besides, the CKS2 expression was also found to have significant correlations with immunity cycle steps and diverse immune markers in HCC. The high CKS2 expression was confirmed in HCC at both mRNA and protein levels, showing a significant increase compared to normal tissue.
Conclusion: CKS2 is a potential prognostic biomarker of HCC and can promote the progression of HCC via its influences on the immune environment. Additionally, a positive correlation between CKS2 and immune markers was observed, highlighting its potential as an immunotherapeutic target.
Keywords: CKS2; hepatocellular carcinoma; immune cycle; immune markers; immunomodulators; tumor immune microenvironment.
© 2023 Zhi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Biological functions and therapeutic potential of CKS2 in human cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 12;14:1424569. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1424569. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39188686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Regulatory Subunit 2 Indicated Poor Prognosis and Facilitated Aggressive Phenotype of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Dis Markers. 2019 Oct 22;2019:8964015. doi: 10.1155/2019/8964015. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31781310 Free PMC article.
-
CKS2 Overexpression Correlates with Prognosis and Immune Cell Infiltration in Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Comprehensive Study based on Bioinformatics and Experiments.J Cancer. 2021 Oct 11;12(23):6964-6978. doi: 10.7150/jca.63625. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34729099 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance and expression of cyclin kinase subunits 1 and 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Int. 2010 Jan;30(1):119-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02106.x. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Liver Int. 2010. PMID: 19845855
-
CPNE1 is a potential prognostic biomarker, associated with immune infiltrates and promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Feb 9;22(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02485-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35139863 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of cyclin-dependent kinase subunit 2 (CKS2) in malignant tumours: a meta-analysis and bioinformatic analysis.BMJ Open. 2024 Jan 31;14(1):e073887. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-073887. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38296306 Free PMC article.
-
Biological functions and therapeutic potential of CKS2 in human cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 12;14:1424569. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1424569. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39188686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress on the Role of Epigenetic Methylation Modification in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jun 17;11:1143-1156. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S458734. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38911291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Transport Receptor Importin-β Inhibition Enhances Cell Cycle Arrest Induced by CKS2 Knockdown to Suppress Neuroblastoma Progression.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jul 22;50(4):245. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04488-7. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40696188
-
DNMT1 blocks SOX21-repressed CKS2 transcription to promote gastric cancer progression.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 17;25(1):1182. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14577-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40676553 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

