Online health community-An empirical analysis based on grounded theory and entropy weight TOPSIS method to evaluate the service quality
- PMID: 37841514
- PMCID: PMC10571705
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076231207201
Online health community-An empirical analysis based on grounded theory and entropy weight TOPSIS method to evaluate the service quality
Abstract
Introduction: With the enhancement of people's health awareness and the impact of the coronavirus pandemic in recent years, people's demand for online health information continues to expand, and online health communities (OHCs) have developed rapidly. However, the service quality of OHCs is uneven, and problems such as content quality, privacy disclosure are increasingly prominent. It's of great significance to establish normalized OHC service quality evaluation standards and develop effective evaluation tools and methods for the improvement of OHC service quality.
Material and methods: Based on the grounded theory, the raw materials obtained from semi-structured interviews were coded in three stages to construct a service quality evaluation system for OHC. Through empirical analysis, the rationality and effectiveness of the evaluation system were verified. Then six representative Chinese OHCs were selected and their service quality was evaluated by the entropy weight TOPSIS method.
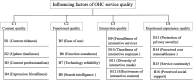
Results: The service quality evaluation system of OHC was constructed which includes 4 first-level indicators and 16 second-level indicators. The weights of the first-level indicators from large to small are content quality, emotional experience quality, interaction quality and function quality. Among the second-level indicator weights, the top three are perceived cost reasonableness, content professionalism and effectiveness of interactive content.
Conclusions: The indicator system is reasonable and effective and the evaluation method has strong applicability and operability. This study will provide theoretical guidance for community platform operators and relevant departments to design effective evaluation mechanism of OHC service quality, offering a reference for decisions and policymakers.
Keywords: Online health community (OHC); entropy weight TOPSIS method; evaluation; grounded theory; service quality.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of community basic public health service effect in a city in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region--based on entropy weight TOPSIS method and RSR fuzzy set.Arch Public Health. 2023 Aug 17;81(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13690-023-01151-x. Arch Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37592329 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Health Information Privacy Concerns on Engagement and Payment Behaviors in Online Health Communities.Front Psychol. 2022 Apr 8;13:861903. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.861903. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35465543 Free PMC article.
-
Collective Empowerment in Online Health Communities: Scale Development and Empirical Validation.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Nov 20;21(11):e14392. doi: 10.2196/14392. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31746772 Free PMC article.
-
Youth violence intervention programme for vulnerable young people attending emergency departments in London: a rapid evaluation.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023 Jul;11(10):1-122. doi: 10.3310/JWKT0492. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023. PMID: 37470144
-
Multi-gene Pharmacogenomic Testing That Includes Decision-Support Tools to Guide Medication Selection for Major Depression: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021 Aug 12;21(13):1-214. eCollection 2021. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021. PMID: 34484487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnston AC, Worrell JL, Di Gangi PM, et al. Online health communities. Inf Technol People 2013; 26: 213–235.
-
- Chen Q, Jin J, Yan X. Understanding online review behaviors of patients in online health communities: an expectation-disconfirmation perspective. Inf Technol People 2022; 35: 2441–2469.
-
- General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. Opinions on promoting the development of “Internet + medical health”, http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2018-04/28/content_5286645.htm (2018, accessed 10 October 2022).
-
- Ministry of industry and Information Technology of the people's Republic of China, National Health Commission of the people's Republic of China. Notice on further strengthening the capacity building of telemedicine networks, http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-11/04/content_5557432.htm (2020, accessed 12 October 2022).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources