Management of Glucose-Lowering Therapy in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: Challenges and Opportunities
- PMID: 37841649
- PMCID: PMC10573466
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S423122
Management of Glucose-Lowering Therapy in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
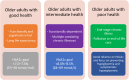
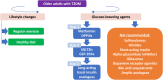
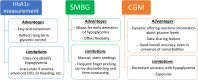
The population of older adults (≥65 years) with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is diverse, encompassing individuals with varying functional capabilities, living arrangements, concomitant medical conditions, and life expectancies. Hence, their categorization into different patient profiles (ie, good health, intermediate health, poor health) may aid in clinical decision-making when establishing glycemic goals and pharmacological treatment strategies. Further granularity in assessing each patient profile through interdisciplinary collaboration may also add precision to therapeutic and monitoring decisions. In this review, we discuss with a multidisciplinary approach how to deliver the best benefit from advanced diabetes therapies and technologies to older adults with T2DM according to each patient profile. There remain however several areas that deserve further research in older adults with T2DM, including the efficacy and safety of continuous glucose monitoring and automated insulin delivery systems, the switch to once-weekly insulin, the effectiveness of multidisciplinary care models, and the use of supported telemedicine and remote blood glucose monitoring in the oldest-old (≥85 years) who particularly require the assistance of others.
Keywords: management; older adults; patient profiles; type 2 diabetes.
© 2023 Doucet et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Jean Doucet has received occasional fees, either personally or institutionally, for the activities of speaking or scientific advising from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Pierre Gourdy has received occasional fees, either personally or institutionally, for the activities of speaking, scientific advising, or clinical research from Abbott, Amarin, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novo Nordisk, Organon, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Laurent Meyer has received occasional fees, either personally or institutionally, for the activities of speaking, scientific advising, or clinical research from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Servier, Medtronic, and Isis Diabète. Nabil Benabdelmoumene has received occasional fees, either personally or institutionally, from AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Eli Lilly. Isabelle Bourdel-Marchasson has received occasional fees from Novo-Nordisk for activities of speaking or scientific advising. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automated Insulin Delivery Systems as a Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review.Endocr Pract. 2023 Mar;29(3):214-220. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2022.10.001. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Endocr Pract. 2023. PMID: 36241017 Review.
-
Assessing the Therapeutic Utility of Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 2 Diabetes Across Various Therapies: A Retrospective Evaluation.Adv Ther. 2017 Aug;34(8):1918-1927. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0576-x. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Adv Ther. 2017. PMID: 28667580
-
Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):935-82. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8529(05)70222-x. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001. PMID: 11727406 Review.
-
Short-term intensive insulin therapy could be the preferred option for new onset Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with HbA1c > 9.J Diabetes. 2017 Oct;9(10):890-893. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12581. Epub 2017 Aug 22. J Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28661564
-
Management of hypoglycemia in older adults with type 2 diabetes.Postgrad Med. 2019 May;131(4):241-250. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2019.1578590. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Postgrad Med. 2019. PMID: 30724638 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors affecting suboptimal maturation of autogenous arteriovenous fistula in elderly patients with diabetes:A narrative review.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 3;10(15):e35766. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35766. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing the Hidden Impacts: Insights into Biological Aging and Long-Term Effects in Pauci- and Asymptomatic COVID-19 Healthcare Workers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 24;25(15):8056. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158056. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125624 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of Insulin Glargine 300 U/ML: Does It Really Matter in Terms of Efficacy and Safety at Insulin Initiation?Cureus. 2025 Mar 4;17(3):e80050. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80050. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40190894 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Jordan: The PACT-MEA Study.Diabetes Ther. 2025 May;16(5):899-913. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01718-7. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Diabetes Ther. 2025. PMID: 40106223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orimo H, Ito H, Suzuki T, Araki A, Hosoi T, Sawabe M. Reviewing the definition of “elderly”. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2006;6(3):149–158. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0594.2006.00341.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

