Research status of facial nerve repair
- PMID: 37841661
- PMCID: PMC10570629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reth.2023.09.012
Research status of facial nerve repair
Abstract
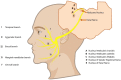
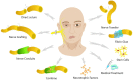
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, is critical in controlling the movement of the facial muscles. It is responsible for all facial expressions, such as smiling, frowning, and moving the eyebrows. However, damage to this nerve can occur for a variety of reasons, including maxillofacial surgery, trauma, tumors, and infections. Facial nerve injuries can cause severe functional impairment and can lead to different degrees of facial paralysis, significantly affecting the quality of life of patients. Over the past ten years, significant progress has been made in the field of facial nerve repair. Different approaches, including direct suture, autologous nerve grafts, and tissue engineering, have been utilized for the repair of facial nerve injury. This article mainly summarizes the clinical methods and basic research progress of facial nerve repair in the past ten years.
Keywords: Facial nerve; Maxillofacial surgery; Regeneration; Repair.
© 2023 The Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors disclosed no relevant relationships.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Anatomic Landmark Approach to Extratemporal Facial Nerve Repair in Facial Trauma.Cureus. 2022 Mar 3;14(3):e22787. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22787. eCollection 2022 Mar. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35382176 Free PMC article.
-
One-stage dual latissimus dorsi muscle flap transfer with a pair of vascular anastomoses and double nerve suturing for long-standing facial paralysis.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015 Jun;68(6):e113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Feb 21. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015. PMID: 25819029
-
Facial Nerve Repair: Bioengineering Approaches in Preclinical Models.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022 Apr;28(2):364-378. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2020.0381. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022. PMID: 33632013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five-Year Experience with Fifth-to-Seventh Nerve Transfer for Smile.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019 May;143(5):1060e-1071e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005591. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019. PMID: 31033832
-
[FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS - THERAPEUTIC APPROACH, FACIAL REANIMATION AND ADJUNCTIVE TREATMENT].Harefuah. 2020 Aug;159(8):612-617. Harefuah. 2020. PMID: 32852164 Review. Hebrew.
Cited by
-
A biodegradable and flexible neural interface for transdermal optoelectronic modulation and regeneration of peripheral nerves.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 3;15(1):4721. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49166-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38830884 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose-derived stem cells in fat grafting for facial paralysis: A review of their therapeutic modality.JPRAS Open. 2025 Feb 17;44:145-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2025.01.019. eCollection 2025 Jun. JPRAS Open. 2025. PMID: 40212106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Analysis of the effect of different facial nerve managements applied to tumor resection in the jugular foramen region].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 May;38(5):368-371;375. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.05.003. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38686470 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
LncRNA GAS5 modulates Schwann cell function and enhances facial nerve injury repair via the miR-138-5p/CXCL12 axis.J Mol Histol. 2024 Oct;55(5):741-752. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10227-z. Epub 2024 Jul 28. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39068616
-
Optimizing Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: Surgical Techniques, Biomolecular and Regenerative Strategies-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 20;26(8):3895. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083895. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kochhar A., Larian B., Azizzadeh B. Facial nerve and parotid gland anatomy. Otolaryngol Clin. 2016;49(2):273–284. - PubMed
-
- George E., Richie M.B., Glastonbury C.M. Facial nerve palsy: clinical practice and cognitive errors. Am J Med. 2020;133(9):1039–1044. - PubMed
-
- Akinrodoye M.A., Lui F. StatPearls; Treasure Island (FL): 2023. Neuroanatomy, somatic nervous system. - PubMed
-
- Veillona F., Ramos-Taboada L., Abu-Eid M., Charpiot A., Riehm S. Imaging of the facial nerve. Eur J Radiol. 2010;74(2):341–348. - PubMed
-
- Spencer C.R., Irving R.M. Causes and management of facial nerve palsy. Br J Hosp Med. 2016;77(12):686–691. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous