Radio-pathomic approaches in pediatric neuro-oncology: Opportunities and challenges
- PMID: 37841693
- PMCID: PMC10576517
- DOI: 10.1093/noajnl/vdad119
Radio-pathomic approaches in pediatric neuro-oncology: Opportunities and challenges
Abstract
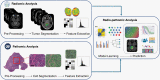
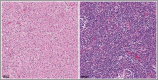
With medical software platforms moving to cloud environments with scalable storage and computing, the translation of predictive artificial intelligence (AI) models to aid in clinical decision-making and facilitate personalized medicine for cancer patients is becoming a reality. Medical imaging, namely radiologic and histologic images, has immense analytical potential in neuro-oncology, and models utilizing integrated radiomic and pathomic data may yield a synergistic effect and provide a new modality for precision medicine. At the same time, the ability to harness multi-modal data is met with challenges in aggregating data across medical departments and institutions, as well as significant complexity in modeling the phenotypic and genotypic heterogeneity of pediatric brain tumors. In this paper, we review recent pathomic and integrated pathomic, radiomic, and genomic studies with clinical applications. We discuss current challenges limiting translational research on pediatric brain tumors and outline technical and analytical solutions. Overall, we propose that to empower the potential residing in radio-pathomics, systemic changes in cross-discipline data management and end-to-end software platforms to handle multi-modal data sets are needed, in addition to embracing modern AI-powered approaches. These changes can improve the performance of predictive models, and ultimately the ability to advance brain cancer treatments and patient outcomes through the development of such models.
Keywords: neuro-oncology; pathomics; pediatrics; radio-pathomics; radiomics.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press, the Society for Neuro-Oncology and the European Association of Neuro-Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Personalized Breast Cancer Treatments Using Artificial Intelligence in Radiomics and Pathomics.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2019 Dec;50(4 Suppl 2):S32-S41. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2019.07.010. Epub 2019 Aug 22. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2019. PMID: 31447230
-
[Artificial intelligence, radiomics and pathomics to predict response and survival of patients treated with radiations].Cancer Radiother. 2021 Oct;25(6-7):630-637. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2021.06.027. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Cancer Radiother. 2021. PMID: 34284970 Review. French.
-
An advanced molecular medicine case report of a rare human tumor using genomics, pathomics, and radiomics.Front Genet. 2023 Feb 10;13:987175. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.987175. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36846293 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Cross-Scale Associations between Radiomic and Pathomic Signatures of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes: Preliminary Results.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 7;12(12):3663. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123663. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33297357 Free PMC article.
-
Potential and limitations of radiomics in neuro-oncology.J Clin Neurosci. 2021 Aug;90:206-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2021.05.015. Epub 2021 Jun 11. J Clin Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34275550 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Institutional Development and Validation of a Radiomic Model to Predict Prostate Cancer Recurrence Following Radical Prostatectomy.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 26;12(23):7322. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237322. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38068372 Free PMC article.
-
Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography-Derived Radiomic Models in Prostate Cancer Prognostication.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 16;16(10):1897. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101897. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of AI Decision Support on Clinical Experts' Radiographic Interpretation of Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2025 May 22;2024:930-939. eCollection 2024. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2025. PMID: 40417524 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics in pediatric brain tumors: from images to insights.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 15;16(1):1563. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03391-5. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40817158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
