A Type 1 Diabetes Polygenic Score Is Not Associated With Prevalent Type 2 Diabetes in Large Population Studies
- PMID: 37841955
- PMCID: PMC10576255
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvad123
A Type 1 Diabetes Polygenic Score Is Not Associated With Prevalent Type 2 Diabetes in Large Population Studies
Abstract
Context: Both type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) have significant genetic contributions to risk and understanding their overlap can offer clinical insight.
Objective: We examined whether a T1D polygenic score (PS) was associated with a diagnosis of T2D in the Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) consortium.
Methods: We constructed a T1D PS using 79 known single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with T1D risk. We analyzed 13 792 T2D cases and 14 169 controls from CHARGE cohorts to determine the association between the T1D PS and T2D prevalence. We validated findings in an independent sample of 2256 T2D cases and 27 052 controls from the Mass General Brigham Biobank (MGB Biobank). As secondary analyses in 5228 T2D cases from CHARGE, we used multivariable regression models to assess the association of the T1D PS with clinical outcomes associated with T1D.
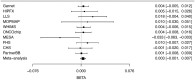
Results: The T1D PS was not associated with T2D both in CHARGE (P = .15) and in the MGB Biobank (P = .87). The partitioned human leukocyte antigens only PS was associated with T2D in CHARGE (OR 1.02 per 1 SD increase in PS, 95% CI 1.01-1.03, P = .006) but not in the MGB Biobank. The T1D PS was weakly associated with insulin use (OR 1.007, 95% CI 1.001-1.012, P = .03) in CHARGE T2D cases but not with other outcomes.
Conclusion: In large biobank samples, a common variant PS for T1D was not consistently associated with prevalent T2D. However, possible heterogeneity in T2D cannot be ruled out and future studies are needed do subphenotyping.
Keywords: genetics; polygenic score; type 1 diabetes; type 2 diabetes.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association . 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Medical Care In Diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43(Suppl 1):S14‐S31. - PubMed
-
- Farmer A, Fox R. Diagnosis, classification, and treatment of diabetes. BMJ. 2011;342:d3319. - PubMed
-
- Tuomi T, Groop LC, Zimmet PZ, Rowley MJ, Knowles W, Mackay IR. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase reveal latent autoimmune diabetes mellitus in adults with a non-insulin-dependent onset of disease. Diabetes. 1993;42(2):359‐362. - PubMed
-
- Palmer JP, Hirsch IB. What's in a name: latent autoimmune diabetes of adults, type 1.5, adult-onset, and type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(2):536‐538. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 75N92021D00005/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00004/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL103612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK120932/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK114551/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00003/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92019D00031/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151855/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL157960/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
