Statins markedly potentiate aminopeptidase inhibitor activity against (drug-resistant) human acute myeloid leukemia cells
- PMID: 37842233
- PMCID: PMC10571057
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2023.20
Statins markedly potentiate aminopeptidase inhibitor activity against (drug-resistant) human acute myeloid leukemia cells
Abstract
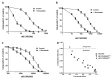
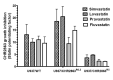
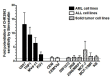
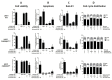
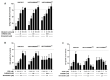
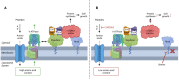
Aim: This study aimed to decipher the molecular mechanism underlying the synergistic effect of inhibitors of the mevalonate-cholesterol pathway (i.e., statins) and aminopeptidase inhibitors (APis) on APi-sensitive and -resistant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Methods: U937 cells and their sublines with low and high levels of acquired resistance to (6S)-[(R)-2-((S)-Hydroxy-hydroxycarbamoyl-methoxy-methyl)-4-methyl-pentanoylamino]-3,3 dimethyl-butyric acid cyclopentyl ester (CHR2863), an APi prodrug, served as main AML cell line models. Drug combination effects were assessed with CHR2863 and in vitro non-toxic concentrations of various statins upon cell growth inhibition, cell cycle effects, and apoptosis induction. Mechanistic studies involved analysis of Rheb prenylation required for mTOR activation. Results: A strong synergy of CHR2863 with the statins simvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, and pravastatin was demonstrated in U937 cells and two CHR2863-resistant sublines. This potent synergy between simvastatin and CHR2863 was also observed with a series of other human AML cell lines (e.g., THP1, MV4-11, and KG1), but not with acute lymphocytic leukemia or multiple solid tumor cell lines. This synergistic activity was: (i) specific for APis (e.g., CHR2863 and Bestatin), rather than for other cytotoxic agents; and (ii) corroborated by enhanced induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest which increased the sub-G1 fraction. Consistently, statin potentiation of CHR2863 activity was abrogated by co-administration of mevalonate and/or farnesyl pyrophosphate, suggesting the involvement of protein prenylation; this was experimentally confirmed by impaired Rheb prenylation by simvastatin. Conclusion: These novel findings suggest that the combined inhibitory effect of impaired Rheb prenylation and CHR2863-dependent mTOR inhibition instigates a potent synergistic inhibition of statins and APis on human AML cells.
Keywords: Aminopeptidase; Rheb; carboxyl esterase; mTOR; mevalonate pathway; statins.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
A preliminary account of this work was presented at the 2018 Annual Meeting of the American Society for Hematology (J. Cloos et al. Blood, vol 132, Supplement 1, Nov 2018, p 3945, abstract).
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
