Effects of Quercetin Nanoemulsion on Cholesterol Efflux and MicroRNA-33/34a Expression in the Liver of Mice Fed with a High-Cholesterol Diet
- PMID: 37842255
- PMCID: PMC10567602
- DOI: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.3.271
Effects of Quercetin Nanoemulsion on Cholesterol Efflux and MicroRNA-33/34a Expression in the Liver of Mice Fed with a High-Cholesterol Diet
Abstract
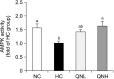
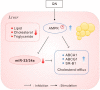
Quercetin is a flavonoid widely present in plants; despite its beneficial physiological activity, it exhibits considerably low bioavailability. Nanoemulsion technology is used for improving the bioavailability of lipophilic phenolic compounds. This study aimed to investigate the potential effects of quercetin nanoemulsion (QN) on regulating the microRNA (miR)-33/34a pathway involved in cholesterol efflux in the liver of mice fed with a high-cholesterol (HC) diet. Subsequently, C57BL/6J mice were divided into four groups and fed a normal chow diet, HC diet supplemented with 1% cholesterol and 0.5% cholic acid, or HC diet supplemented with 0.05% QN or 0.1% QN for 6 weeks. Serum and hepatic lipid profiles were assayed using commercial enzymatic kits. Gene expression and miR levels were quantified using real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, and adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity was measured using an AMPK Kinase Assay kit. QN supplementation improved serum and liver lipid profiles. QN upregulated the mRNA levels of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette subfamily A1, ATP-binding cassette subfamily G1, and scavenger receptor class B type 1, which are related to cholesterol efflux. In the QN group, the hepatic AMPK activity increased, whereas miR-33, and miR-34a expression levels decreased. These results suggest that QN may enhance cholesterol efflux, at least partly through modulating AMPK activity and miR-33/34a expression in the liver.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; cholesterol; microRNAs; quercetin.
Copyright © 2023 by The Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHOR DISCLOSURE STATEMENT The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Portulaca oleracea L. Extract Regulates Hepatic Cholesterol Metabolism via the AMPK/MicroRNA-33/34a Pathway in Rats Fed a High-Cholesterol Diet.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 14;14(16):3330. doi: 10.3390/nu14163330. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014836 Free PMC article.
-
Pine (Pinus koraiensis) Nut Oil Ameliorates Cholesterol Homeostasis and Inflammation via Modulating the miR-34a/122 Pathways in the Liver of Rats Fed a High-Cholesterol Diet.J Nutr. 2025 Mar;155(3):871-879. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2025.01.018. Epub 2025 Jan 20. J Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39842550
-
High hydrostatic pressure extract of mulberry leaves ameliorates hypercholesterolemia via modulating hepatic microRNA-33 expression and AMPK activity in high cholesterol diet fed rats.Food Nutr Res. 2021 May 3;65. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v65.7587. eCollection 2021. Food Nutr Res. 2021. PMID: 33994909 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin regulates hepatic cholesterol metabolism by promoting cholesterol-to-bile acid conversion and cholesterol efflux in rats.Nutr Res. 2016 Mar;36(3):271-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2015.11.019. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Nutr Res. 2016. PMID: 26923514
-
Macrophage miR-34a Is a Key Regulator of Cholesterol Efflux and Atherosclerosis.Mol Ther. 2020 Jan 8;28(1):202-216. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.09.008. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31604677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cui Y, Hou P, Li F, Liu Q, Qin S, Zhou G, et al. Quercetin improves macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice fed a high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2017;16:9. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0393-2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-016-0393-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
