Remnant cholesterol associates with hypertension beyond low-density lipoprotein cholesterol among the general US adult population
- PMID: 37842298
- PMCID: PMC10570462
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1260764
Remnant cholesterol associates with hypertension beyond low-density lipoprotein cholesterol among the general US adult population
Abstract
Background: Previous findings have indicated that elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and remnant cholesterol (RC) are associated with hypertension. We aim to explore whether higher RC levels may be associated with hypertension beyond LDL-C in the general US adult population.
Methods: This study included 10,842 adults from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2018. Weighted multivariable logistic regression models were used to estimate the odds ratios (ORs) of hypertension for LDL-C and RC. We also performed analyses examining the association between hypertension and LDL-C vs. RC concordant/discordant groups.
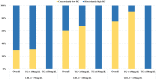
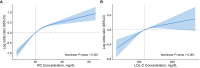
Results: A total of 4,963 (41.54%, weighted) individuals had hypertension. The weighted median levels were LDL-C: 118mg/dL, RC: 20mg/dL. At lower LDL-C clinical cut-point, the proportion of discordantly high RC dramatically increased. After multivariable adjustment, log RC was associated with higher prevalence of hypertension [OR 2.54, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2.17-2.99]. Participants with the highest tertile of RC were more likely to have hypertension (OR 2.18; 95% CI 1.89-2.52) compared with those with the lowest tertile of RC. This association remained marked after including body mass index (BMI), LDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) or triglycerides. The association between LDL-C and hypertension was absent after adjusting for BMI, RC or triglycerides. Compared with low LDL-C/low RC group, the discordant low LDL-C/high RC group was associated with hypertension (OR 2.04; 95% CI 1.72-2.42), whereas the high LDL-C/low RC group was not, regardless of BMI, HDL-C or triglycerides. Similar results were observed when examining discordance among different clinical cut-points, except for the cut-point of LDL-C 70 mg/dL and RC 13 mg/dL. To better understand the association, we performed an additional analysis, which showed that among participants with apolipoprotein B < median (92mg/dL), those with discordant RC ≥ median (20mg/dL) had significantly higher odds of having hypertension (OR 1.73; 95% CI 1.38-2.17).
Conclusion: RC was associated with hypertension beyond LDL-C in the general US adult population. This association went beyond increased triglycerides levels, and lipoproteins other than apoB may be involved.
Keywords: apolipoprotein B; dyslipidemia; hypertension; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; remnant cholesterol.
Copyright © 2023 Shi, Zhang, Ju, Wang, Du, Chen, Song, Gao and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Xu J, Arias E. Deaths: final data for 2017. Natl Vital Stat Rep (2019) 68(9):1–77. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Hypertension Cascade: Hypertension Prevalence, Treatment and Control Estimates among U.S. Adults Aged 18 Years and Older. Available at: https://Millionhearts.Hhs.Gov/Data-Reports/Hypertension-Prevalence.Html (Accessed March 22, 2021).
-
- Nelson S, Whitsel L, Khavjou O, Phelps D, Leib A. Projections of cardiovascular disease prevalence and costs: 2015-2035. Tech Rep Res Triangle Park, NC, USA: RTI Int; (2016) Rti Project No. 0214680.003.001.001. Available at: https://www.heart.org/-/media/Files/Get-Involved/Advocacy/CVD-Prediction....
-
- Handelsman Y, Jellinger PS, Guerin CK, Bloomgarden ZT, Brinton EA, Budoff MJ, et al. . Consensus statement by the American association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology on the management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease algorithm - 2020 executive summary. Endocr Pract (2020) 26(10):1196–224. doi: 10.4158/CS-2020-0490 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

