Causes and Prevention of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 37842356
- PMCID: PMC10569084
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.45095
Causes and Prevention of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
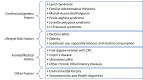
Sporadic colorectal cancer (CRC) has historically been considered a disease of the elderly. However, early-onset colorectal cancer (eoCRC) incidence and prevalence have steadily increased over the last few decades, highlighting the critical need for a comprehensive understanding of its causes and prevention. This research examines the numerous factors contributing to the increasing incidence of eoCRC. These factors include a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental effects. We also investigate the impact of modifiable lifestyle factors like obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet on eoCRC risk. Understanding these factors is critical in developing future diagnostic, prognostic, disease monitoring, and therapy planning strategies in managing eoCRC and will help optimize guidelines for CRC screening.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; diet; early-onset; lifestyle; prevention; risk factors; sporadic.
Copyright © 2023, Adigun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Perspective Review on Diet Quality, Excess Adiposity, and Chronic Psychosocial Stress and Implications for Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer.J Nutr. 2024 Apr;154(4):1069-1079. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.03.002. Epub 2024 Mar 6. J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38453027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology and biology of early onset colorectal cancer.EXCLI J. 2022 Jan 7;21:162-182. doi: 10.17179/excli2021-4456. eCollection 2022. EXCLI J. 2022. PMID: 35221839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer.Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2022 Apr;31(2):143-155. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2021.11.001. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2022. PMID: 35351270 Review.
-
Focusing on colorectal cancer in young adults (Review).Mol Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec 6;20(1):8. doi: 10.3892/mco.2023.2706. eCollection 2024 Jan. Mol Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38125745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diet and Lifestyle Habits in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer: A Pilot Case-Control Study.Dig Dis. 2022;40(6):710-718. doi: 10.1159/000521932. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Dig Dis. 2022. PMID: 35086089
Cited by
-
Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid exposure leads to downregulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 expression and upregulation of markers associated with intestinal carcinogenesis in mouse intestinal tissues.Chemosphere. 2024 Jul;359:142332. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.142332. Epub 2024 May 14. Chemosphere. 2024. PMID: 38754493 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Dietary Vitamins and Antioxidants in Preventing Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Jul 10;16(7):e64277. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64277. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39130946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights from age-stratified endoscopic detection metrics support initiating colorectal cancer screening at age 45.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 19;25(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04213-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40830845 Free PMC article.
-
Closing Editorial: Colorectal Cancer-A Molecular Genetics Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 24;25(23):12604. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312604. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684316 Free PMC article.
-
Rising Incidence and Mortality of Colorectal Cancer in Young African Adults: Need for a Better Care Plan.Cureus. 2025 Jun 12;17(6):e85866. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85866. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40656337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:233–254. - PubMed
-
- Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence in young adults. Siegel RL, Torre LA, Soerjomataram I, Hayes RB, Bray F, Weber TK, Jemal A. Gut. 2019;68:2179–2185. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources