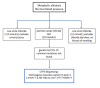
Uncommon Presentation of Cystic Fibrosis: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 37842418
- PMCID: PMC10575793
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.45186
Uncommon Presentation of Cystic Fibrosis: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a multiorgan disease, caused by autosomal recessive (AR) mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) acting primarily as a chloride channel. CF is most commonly diagnosed in Caucasian populations. Common clinical presentations in pediatric patients include chronic cough, respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia, digestive symptoms, and stunted growth, and malnutrition due to gastrointestinal malabsorption and pancreatic insufficiency. Excessive sweat sodium chloride losses due to dysfunctional sweat glands in CFTR result in volume contraction and secondary hyperaldosteronism leading to renal potassium losses and metabolic alkalosis. Hypokalemic hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis is a known but uncommon presenting sign of the disease, documented as pseudo Bartter syndrome. Common mutations in the CFTR gene are now included in prenatal genetic screening programs. We describe the case of an infant of African descent with normal prenatal screening who presented with severe hypokalemic hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis and was diagnosed with CF with further genetic confirmation of the diagnosis.
Keywords: cystic fibrosis (cf); genetic screening; hypokalemic hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis; hyponatremia; • dehydration.
Copyright © 2023, Abu Sirhan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical characterization and diagnosis of cystic fibrosis through exome sequencing in Chinese infants with Bartter-syndrome-like hypokalemia alkalosis.Front Med. 2018 Oct;12(5):550-558. doi: 10.1007/s11684-017-0567-y. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Front Med. 2018. PMID: 29520692
-
[Chinese experts consensus statement: diagnosis and treatment of cystic fibrosis (2023)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2023 Apr 12;46(4):352-372. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20221214-00971. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36990700 Chinese.
-
Cystic fibrosis presenting with hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis in a previously healthy adolescent.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997 Feb;8(2):352-5. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V82352. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997. PMID: 9048354
-
Cystic Fibrosis Presenting as Pseudo-Bartter Syndrome: An Important Diagnosis that is Missed!Indian J Pediatr. 2020 Sep;87(9):726-732. doi: 10.1007/s12098-020-03342-8. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Indian J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32504456 Review.
-
[Cystic fibrosis primarily presenting with pseudo-Bartter syndrome: a report of three cases and literature review].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 May 15;26(5):506-511. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2310080. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38802912 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Clinical Disorders in Cystic Fibrosis That Affect Emergency Procedures-A Case Report and Review.J Clin Med. 2025 May 5;14(9):3187. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093187. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40364218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cystic Fibrosis Newborn Screening: A Systematic Review-Driven Consensus Guideline from the United States Cystic Fibrosis Foundation.Int J Neonatal Screen. 2025 Apr 2;11(2):24. doi: 10.3390/ijns11020024. Int J Neonatal Screen. 2025. PMID: 40265445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cystic fibrosis: presentation with other diseases, the experience in Saudi Arabia. Banjar H. J Cyst Fibros. 2003;2:155–159. - PubMed
-
- Highly variable incidence of cystic fibrosis and different mutation distribution among different Jewish ethnic groups in Israel. Kerem E, Kalman YM, Yahav Y, et al. Hum Genet. 1995;96:193–197. - PubMed
-
- An epidemic of pseudo-Bartter syndrome in cystic fibrosis patients. Kose M, Pekcan S, Ozcelik U, Cobanoglu N, Yalcin E, Dogru D, Kiper N. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-007-0413-3. Eur J Pediatr. 2008;167:115–116. - PubMed
-
- Declining prevalence of cystic fibrosis since the introduction of newborn screening. Massie J, Curnow L, Gaffney L, Carlin J, Francis I. Arch Dis Child. 2010;95:531–533. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials