Efficacy and mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong pill on the prevention and treatment of EAE
- PMID: 37842634
- PMCID: PMC10568116
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20621
Efficacy and mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong pill on the prevention and treatment of EAE
Abstract
Objective: Studies have shown that Wuzi Yanzong Pill (WYP) can be used to treat neurological diseases, but its mechanisms for multiple sclerosis (MS) remain unclear. This study aims to determine the effect of WYP on MS in an animal model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), and explore its mechanism. To provide theoretical basis for the clinical treatment of MS with WYP.
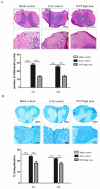
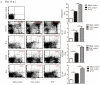
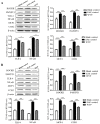
Methods: C57BL/6 female mice were randomly divided into Blank control, EAE control, low dose WYP, medium dose WYP, and high dose WYP groups. One week before model generation, the mice were gavaged with saline (50 mL/kg/d) in Blank control and EAE control groups. The treatment groups was gavaged with different doses of WYP solution (4, 8, or 16 g/kg/d respectively) Clinical scores were recorded daily. Sample collection was conducted on the 14th and 28th days, respectively The expressions of IL-10, IL-17, IL-12, TNF-α and IFN-γ in spleen were detected by ELISA. The expressions of ROCKII, P-MYPT1, TLR4, NF-κB/p65, MCP-1, CCR2 in spleen, brain and spinal cord were detected by Western Blot. The types of macrophages and the contents of intracellular IL-10 and IL-12 were detected by Flow Cytometry. The contents of TNF-α and TLR4 mRNA in the spleen were detected by RT-PCR.
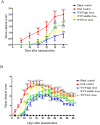
Results: WYP treatment improved the clinical score of EAE mice in a significant dose-dependent manner, with the WYP high-dose group showed the most significant improvement in clinical score. Compared with the EAE control group, WYP high dose group had significantly lower levels of IL-17, IFN-γ, ROCKII, P-MYPT1, TLR4, NF-κB/p65, MCP-1, and CCR2 as well as TNF-α and TLR4 mRNA, but increased the number of M2 macrophages and IL-10.
Conclusion: WYP treatment relieves clinical symptoms in EAE mice, which may be related to regulate inflammatory pathway and inhibiting expressions of inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; Immunomodulation; Wuzi Yanzong Pill; anti-inflammation.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Wuzi Yanzong Pill relieves CPZ-induced demyelination by improving the microenvironment in the brain.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 10;8(12):e12277. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12277. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36578409 Free PMC article.
-
Wuzi Yanzong Pill relieves MPTP-induced motor dysfunction and neuron loss by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Oct;38(7):2211-2222. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01266-8. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 37470879
-
Wuzi Yanzong Pill Plays A Neuroprotective Role in Parkinson's Disease Mice via Regulating Unfolded Protein Response Mediated by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Jan;29(1):19-27. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-3727-0. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36369612
-
Wuzi Yanzong pill attenuates MPTP-induced Parkinson's Disease via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Jun;37(5):1435-1450. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-00993-8. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35488941
-
Wuzi Yanzong prescription from Traditional Chinese Medicine for male infertility: a narrative review.J Tradit Chin Med. 2023 Apr;43(2):416-428. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20221214.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36994532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Therapeutic Mechanisms of Wuzi Yanzong Pill for Asthenozoospermia: A Synergistic Approach Combining Bioinformatics and Molecular Dynamics.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Aug 9. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01835-x. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40783635
-
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Multi-Organ Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 13;25(10):5303. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105303. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791345 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

