Novel laparo-endoscopic hybrid technique of management of a rare case of duodeno-duodenal intussusception
- PMID: 37843157
- PMCID: PMC11354944
- DOI: 10.4103/jmas.jmas_112_23
Novel laparo-endoscopic hybrid technique of management of a rare case of duodeno-duodenal intussusception
Abstract
We herein report a rare case of duodeno-duodenal intussusception (IS) presenting with obstruction caused by tubulovillous adenoma in an adult with malrotation that was managed by a novel laparoendoscopic hybrid technique. This was done by passing transjejunal nasogastric tube (NG) through one of the ports and manoeuvring it towards the IS. Two hundred and fifty millilitre of saline was flushed by aseptosyringe with pressure connected to the NG. This hydrostatic reduction technique resulted in distension of the jejunal and duodenal loop achieving reduction of IS. Intraoperative endoscopy was performed to exactly localise the mass lesion. The duodenum was kocherised and was delivered through a 4-cm transverse incision. Anterior duodenotomy was performed; the mass was excised; and duodenotomy was closed transversely. An extensive literature search did not show any case report of duodenoduodenal IS being managed by this technique. The combination of novel retrograde decompression and intraoperative endoscopy helped us to manage this rare case by this novel technique.
Copyright © 2023 Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Minimal Access Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
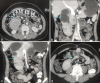
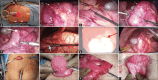
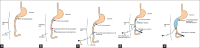
References
-
- Takeuchi K, Tsuzuki Y, Ando T, Sekihara M, Hara T, Kori T, et al. The diagnosis and treatment of adult intussusception. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;36:18–21. - PubMed
-
- Saida Y, Matsueda K, Itai Y. Distal migration of duodenal tumors: Simple prolapse or intussusception? Abdom Imaging. 2002;27:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Huang BY, Warshauer DM. Adult intussusception: Diagnosis and clinical relevance. Radiol Clin North Am. 2003;41:1137–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

