Machine learning applications in stroke medicine: advancements, challenges, and future prospectives
- PMID: 37843210
- PMCID: PMC10664112
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.382228
Machine learning applications in stroke medicine: advancements, challenges, and future prospectives
Abstract
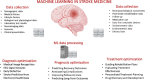
Stroke is a leading cause of disability and mortality worldwide, necessitating the development of advanced technologies to improve its diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes. In recent years, machine learning techniques have emerged as promising tools in stroke medicine, enabling efficient analysis of large-scale datasets and facilitating personalized and precision medicine approaches. This abstract provides a comprehensive overview of machine learning's applications, challenges, and future directions in stroke medicine. Recently introduced machine learning algorithms have been extensively employed in all the fields of stroke medicine. Machine learning models have demonstrated remarkable accuracy in imaging analysis, diagnosing stroke subtypes, risk stratifications, guiding medical treatment, and predicting patient prognosis. Despite the tremendous potential of machine learning in stroke medicine, several challenges must be addressed. These include the need for standardized and interoperable data collection, robust model validation and generalization, and the ethical considerations surrounding privacy and bias. In addition, integrating machine learning models into clinical workflows and establishing regulatory frameworks are critical for ensuring their widespread adoption and impact in routine stroke care. Machine learning promises to revolutionize stroke medicine by enabling precise diagnosis, tailored treatment selection, and improved prognostication. Continued research and collaboration among clinicians, researchers, and technologists are essential for overcoming challenges and realizing the full potential of machine learning in stroke care, ultimately leading to enhanced patient outcomes and quality of life. This review aims to summarize all the current implications of machine learning in stroke diagnosis, treatment, and prognostic evaluation. At the same time, another purpose of this paper is to explore all the future perspectives these techniques can provide in combating this disabling disease.
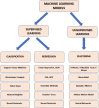
Keywords: cerebrovascular disease; deep learning; machine learning; reinforcement learning; stroke; stroke therapy; supervised learning; unsupervised learning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Realizing the promise of machine learning in precision oncology: expert perspectives on opportunities and challenges.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 17;25(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13621-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39962436 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Pharmacological Research: Bridging the Gap Between Data and Drug Discovery.Cureus. 2023 Aug 30;15(8):e44359. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44359. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37779744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular disease.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Sep 7;17:1254417. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1254417. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37746051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart Smile: Revolutionizing Dentistry With Artificial Intelligence.Cureus. 2023 Jun 30;15(6):e41227. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41227. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37529520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive models for secondary epilepsy in patients with acute ischemic stroke within one year.Elife. 2024 Nov 14;13:RP98759. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98759. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39540824 Free PMC article.
-
The application of artificial intelligence in stroke research: A bibliometric analysis.Digit Health. 2025 Feb 28;11:20552076251323833. doi: 10.1177/20552076251323833. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40027591 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathogenesis of Central and Peripheral Nervous System Complications in Anderson-Fabry Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 20;25(1):61. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010061. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Transforming Neurorehabilitation: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurological Disorders.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 21;12(10):2415. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102415. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a predictive model for postoperative hospitalization time in colorectal cancer patients based on interpretable machine learning algorithm: a prospective preliminary study.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 14;14:1384931. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1384931. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38947887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awan SE, Sohel F, Sanfilippo FM, Bennamoun M, Dwivedi G. Machine learning in heart failure: ready for prime time. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2018;33:190–195. - PubMed
-
- Ayodele T. Types of machine learning algorithms. InTech. doi: 10.5772/9385 2010
-
- Boysen G, Marott JL, Grønbaek M, Hassanpour H, Truelsen T. Long-term survival after stroke: 30 years of follow-up in a cohort the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Neuroepidemiology. 2009;33:254–260. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

