Succinylation modification: a potential therapeutic target in stroke
- PMID: 37843212
- PMCID: PMC10664134
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.382229
Succinylation modification: a potential therapeutic target in stroke
Abstract
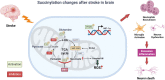
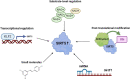
Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and disability worldwide. Ischemic cell death triggered by the compromised supply of blood oxygen and glucose is one of the major pathophysiology of stroke-induced brain injury. Impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism is observed minutes after stroke and is closely associated with the progression of neuropathology. Recently, a new type of post-translational modification, known as lysine succinylation, has been recognized to play a significant role in mitochondrial energy metabolism after ischemia. However, the role of succinylation modification in cell metabolism after stroke and its regulation are not well understood. We aimed to review the effects of succinylation on energy metabolism, reactive oxygen species generation, and neuroinflammation, as well as Sirtuin 5 mediated desuccinylation after stroke. We also highlight the potential of targeting succinylation/desuccinylation as a promising strategy for the treatment of stroke. The succinylation level is dynamically regulated by the nonenzymatic or enzymatic transfer of a succinyl group to a protein on lysine residues and the removal of succinyl catalyzed by desuccinylases. Mounting evidence has suggested that succinylation can regulate the metabolic pathway through modulating the activity or stability of metabolic enzymes. Sirtuins, especially Sirtuin 5, are characterized for their desuccinylation activity and have been recognized as a critical regulator of metabolism through desuccinylating numerous metabolic enzymes. Imbalance between succinylation and desuccinylation has been implicated in the pathophysiology of stroke. Pharmacological agents that enhance the activity of Sirtuin 5 have been employed to promote desuccinylation and improve mitochondrial metabolism, and neuroprotective effects of these agents have been observed in experimental stroke studies. However, their therapeutic efficacy in stroke patients should be validated.
Keywords: mitochondria metabolism; neuroprotection; sirtuin 5; stroke; succinylation modification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging roles of mitochondrial sirtuin SIRT5 in succinylation modification and cancer development.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1531246. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1531246. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39944690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 5-Mediated Lysine Desuccinylation Protects Mitochondrial Metabolism Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice.Stroke. 2021 Dec;52(12):4043-4053. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034850. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 34807744
-
Up-regulated succinylation modifications induce a senescence phenotype in microglia by altering mitochondrial energy metabolism.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Nov 14;21(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03284-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 39543710 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 5 aggravates microglia-induced neuroinflammation following ischaemic stroke by modulating the desuccinylation of Annexin-A1.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Dec 14;19(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02665-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36517900 Free PMC article.
-
Protein succinylation mechanisms and potential targeted therapies in urinary disease.Cell Signal. 2025 Jul;131:111744. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111744. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40090556 Review.
Cited by
-
Lysine succinylation precisely controls normal erythropoiesis.Haematologica. 2025 Feb 1;110(2):397-413. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285752. Haematologica. 2025. PMID: 39415677 Free PMC article.
-
A New Perspective on Stroke Research: Unraveling the Role of Brain Oxygen Dynamics in Stroke Pathophysiology.Aging Dis. 2024 Aug 2;16(4):2343-2353. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0548. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39226161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Neuroprotection after the Intermittent Exposures of Hypercapnic Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 25;25(7):3665. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073665. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of mitochondrial sirtuin SIRT5 in succinylation modification and cancer development.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1531246. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1531246. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39944690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KD_MultiSucc: incorporating multi-teacher knowledge distillation and word embeddings for cross-species prediction of protein succinylation sites.Biol Methods Protoc. 2025 May 28;10(1):bpaf041. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpaf041. eCollection 2025. Biol Methods Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40585181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K, Pistell PJ, Poosala S, Becker KG, Boss O, Gwinn D, Wang M, Ramaswamy S, Fishbein KW, Spencer RG, Lakatta EG, et al. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature. 2006;444:337–342. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beuker C, Strecker JK, Rawal R, Schmidt-Pogoda A, Ruck T, Wiendl H, Klotz L, Schabitz WR, Sommer CJ, Minnerup H, Meuth SG, Minnerup J. Immune cell infiltration into the brain after ischemic stroke in humans compared to mice and rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Stroke Res. 2021;12:976–990. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biasutto L, Mattarei A, Paradisi C. Synthesis and testing of novel isomeric mitochondriotropic derivatives of resveratrol and quercetin. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2275:141–160. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

