Correlation between the gut microbiome and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of metagenomics evidence
- PMID: 37843219
- PMCID: PMC10664138
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.382223
Correlation between the gut microbiome and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of metagenomics evidence
Abstract
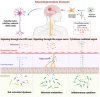
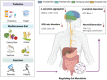
A growing body of evidence suggests that the gut microbiota contributes to the development of neurodegenerative diseases via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. As a contributing factor, microbiota dysbiosis always occurs in pathological changes of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. High-throughput sequencing technology has helped to reveal that the bidirectional communication between the central nervous system and the enteric nervous system is facilitated by the microbiota's diverse microorganisms, and for both neuroimmune and neuroendocrine systems. Here, we summarize the bioinformatics analysis and wet-biology validation for the gut metagenomics in neurodegenerative diseases, with an emphasis on multi-omics studies and the gut virome. The pathogen-associated signaling biomarkers for identifying brain disorders and potential therapeutic targets are also elucidated. Finally, we discuss the role of diet, prebiotics, probiotics, postbiotics and exercise interventions in remodeling the microbiome and reducing the symptoms of neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: biomarker; diet pattern; gut microbiota; gut-brain axis; metagenomics; mitochondrial dysfunction; multi-omics; neurodegenerative disease; neuroinflammation; probiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dysfunction of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neurodegenerative Disease: The Promise of Therapeutic Modulation With Prebiotics, Medicinal Herbs, Probiotics, and Synbiotics.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2020 Jan-Dec;25:2515690X20957225. doi: 10.1177/2515690X20957225. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 33092396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lessons to Learn from the Gut Microbiota: A Focus on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Genes (Basel). 2022 May 12;13(5):865. doi: 10.3390/genes13050865. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut dysbiosis, defective autophagy and altered immune responses in neurodegenerative diseases: Tales of a vicious cycle.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Mar;231:107988. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107988. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34536490 Review.
-
The microbial guardians: Unveiling the role of gut microbiota in shaping neurodegenerative disease.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025 May 30;19:17-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.05.014. eCollection 2025 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40525139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiome-targeted therapies for Alzheimer's disease.Gut Microbes. 2023 Dec;15(2):2271613. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2271613. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 37934614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Strategies for Metabolic Syndrome: How Nutrition, Dietary Polyphenols, Physical Activity, and Lifestyle Modifications Address Diabesity, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Neurodegenerative Conditions.Metabolites. 2024 Jun 11;14(6):327. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060327. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38921462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Genetic, Environmental, and Dietary Factors in Alzheimer's Disease: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 30;26(3):1222. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031222. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects and mechanisms of acupuncture for PIGD-subtype Parkinson's disease via integration of fMRI and gut microbiota-metabolomics analysis: protocol for a prospective randomized controlled trial.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 May 13;17:1534165. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1534165. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40433511 Free PMC article.
-
From Microbial Homeostasis to Systemic Pathogenesis: A Narrative Review on Gut Flora's Role in Neuropsychiatric, Metabolic, and Cancer Disorders.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 5;18:8851-8873. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S531671. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40635765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the molecular and immune interplay between head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma through bioinformatics and machine learning.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):5725-5750. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1064. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39697749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham D, Feher J, Scuderi GL, Szabo D, Dobolyi A, Cservenak M, Juhasz J, Ligeti B, Pongor S, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Vina J, Higuchi M, Suzuki K, Boldogh I, Radak Z. Exercise and probiotics attenuate the development of Alzheimer's disease in transgenic mice: Role of microbiome. Exp Gerontol. 2019;115:122–131. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

