Immunogenicity and safety of a new hexavalent rotavirus vaccine in Chinese infants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial
- PMID: 37843437
- PMCID: PMC10580834
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2263228
Immunogenicity and safety of a new hexavalent rotavirus vaccine in Chinese infants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial
Abstract
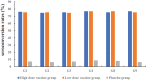
Rotavirus remains a major cause of diarrhea among 5-y-old children, and vaccination is currently the most effective and economical measure. We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II clinical trial designed to determine the dosage, immunogenicity, and safety profile of a novel hexavalent rotavirus vaccine. In total, 480 eligible healthy infants, who were 6-12 weeks of age at the time of randomization were randomly allocated (1:1:1) to receive 105.5 focus-forming unit (FFU) or 106.5FFU of vaccine or placebo on a 0, 28 and 56-d schedule. Blood samples were collected 28 d after the third dose to assess rotavirus immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibody levels. Adverse events (AEs) up to 28 d after each dose and serious adverse events (SAEs) up to 6 months after the third dose were recorded as safety measurements. The anti-rotavirus IgA seroconversion rate of the vaccine groups reached more than 70.00%, ranging from 74.63% to 76.87%. The postdose 3 (PD3) geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) of anti-rotavirus IgA among vaccine recipients ranged from 76.97 U/ml to 84.46 U/ml. At least one solicited AE was recorded in 114 infants (71.25%) in the high-dose vaccine group, 106 infants (66.25%) in the low-dose vaccine group and 104 infants (65.00%) in the placebo group. The most frequently solicited AE was fever. The novel oral hexavalent rotavirus vaccine was safe and immunogenic in infants support the conclusion to advance the candidate vaccine for phase 3 efficacy trials.
Keywords: Rotavirus; immunogenicity; safety; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Qing-Liang Li, Kai Duan, Wei Chen, Ge-Lin Xu, Biao Yang, Ben Dong, and Jiu-Wei Zhang are currently employees of the Wuhan Institute of Biological Products Co., Ltd. Xiao-Ming Yang is currently an employee of China National Biotec Group Co., Ltd., Beijing, China. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and immunogenicity of a novel oral hexavalent rotavirus vaccine:a phase I clinical trial.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021 Jul 3;17(7):2311-2318. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1861874. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33545015 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neonatal rotavirus vaccine (RV3-BB) immunogenicity and safety in a neonatal and infant administration schedule in Malawi: a randomised, double-blind, four-arm parallel group dose-ranging study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 May;22(5):668-678. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00473-4. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35065683 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety, reactogenicity and immunogenicity of the human rotavirus vaccine in preterm European Infants: a randomized phase IIIb study.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 May;31(5):487-93. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182490a2c. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012. PMID: 22228231 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized Phase I/II study to evaluate safety and reactogenicity of a heat-stable rotavirus vaccine in healthy adults followed by evaluation of the safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity in infants.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Mar 3;16(3):693-702. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1664239. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 31526218 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The human rotavirus vaccine RIX4414 in infants: a review of safety and tolerability.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009 Mar;28(3):225-32. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31819715fa. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009. PMID: 19209095 Review.
References
-
- Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Steele AD, Duque J, Parashar UD. 2008 estimate of worldwide rotavirus-associated mortality in children younger than 5 years before the introduction of universal rotavirus vaccination programmes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:136–41. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70253-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous