Integrating mindfulness into the extended process model of emotion regulation: The dual-mode model of mindful emotion regulation
- PMID: 37843512
- PMCID: PMC11009092
- DOI: 10.1037/emo0001308
Integrating mindfulness into the extended process model of emotion regulation: The dual-mode model of mindful emotion regulation
Abstract
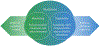
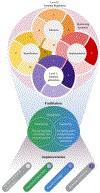
Extensive research has been conducted regarding how people manage their emotions. Within this research, there has been growing attention toward the role of mindfulness in emotion regulation. While prior reviews have discussed mindfulness in the context of emotion regulation, they have not provided a thorough integration using the prevailing models of emotion regulation or mindfulness. The present review discusses the Extended Process Model of Emotion Regulation and Monitoring and Acceptance Theory of mindfulness in order to propose a novel integrated framework, the Dual-mode Model of Mindful Emotion Regulation (D-MER). This model proposes two "modes" of mindfulness: Implementation and facilitation. Implementation posits that mindfulness skills can be used as emotion regulation strategies through attentional deployment and cognitive change. Facilitation posits that mindfulness as a state or trait affects emotion generation and regulation through effects on cognitive processes and positive or negative valence systems. Further, the D-MER posits that mindfulness experience can improve the efficiency of mindfulness-based emotion regulation strategies (implementation) while effects of mindfulness on emotion regulation processes become increasingly trait-like and automatic over time (facilitation). Empirical and theoretical support for this model are discussed, specific hypotheses to guide further research are provided, and clinical implications are presented. Use of this model may identify mechanisms underlying the interaction between mindfulness and emotion regulation which can be used in ongoing affective and clinical research. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2024 APA, all rights reserved).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aldao A, & Christensen K (2015). Linking the expanded process model of emotion regulation to psychopathology by focusing on behavioral outcomes of regulation. Psychological Inquiry, 26(1), 27–36. 10.1080/1047840X.2015.962399 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

