Functional activity of E. coli RNase R in the Antarctic Pseudomonas syringae Lz4W
- PMID: 37843651
- PMCID: PMC10579198
- DOI: 10.1186/s43141-023-00553-2
Functional activity of E. coli RNase R in the Antarctic Pseudomonas syringae Lz4W
Abstract
Background: In Antarctic P. syringae RNase R play an essential role in the processing of 16S and 5S rRNA, thereby playing an important role in cold-adapted growth of the bacterium. This study is focused on deciphering the in vivo functional activity of mesophilic exoribonuclease R and its catalytic domain (RNB) in an evolutionary distant psychrophilic bacterium Pseudomonas syringae Lz4W.
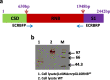
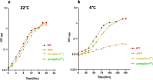
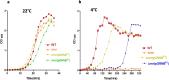
Results: Our results confirm that E. coli RNase R complemented the physiological functions of the psychrophilic bacterium P. syringae RNase R and rescued the cold-sensitive phenotype of Pseudomonas syringae ∆rnr mutant. More importantly, the catalytic domain (RNB) of the E. coli RNase R is also capable of alleviating the cold-sensitive growth defects of ∆rnr mutant as seen with the catalytic domain (RNB) of the P. syringae enzyme. The Catalytic domain of E. coli RNase R was less efficient than the Catalytic domain of P. syringae RNase R in rescuing the cold-sensitive growth of ∆rnr mutant at 4°C, as the ∆rnr expressing the RNBEc (catalytic domain of E. coli RNase R) displayed longer lag phase than the RNBPs (Catalytic domain of P. syringae RNase R) complemented ∆rnr mutant at 4°C. Altogether it appears that the E. coli RNase R and P. syringae RNase R are functionally exchangeable for the growth requirements of P. syringae at low temperature (4°C). Our results also confirm that in P. syringae the requirement of RNase R for supporting the growth at 4°C is independent of the degradosomal complex.
Conclusion: E. coli RNase R (RNase REc) rescues the cold-sensitive phenotype of the P. syringae Δrnr mutant. Similarly, the catalytic domain of E. coli RNase R (RNBEc) is also capable of supporting the growth of Δrnr mutant at low temperatures. These findings have a vast scope in the design and development of low-temperature-based expression systems.
Keywords: Catalytic domain; Cold-adapted enzymes; Degradosome; Exoribonuclease R; Functional complementation; Psychrophiles; RNA processing.
© 2023. Academy of Scientific Research and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A type II toxin-antitoxin system is responsible for the cell death at low temperature in Pseudomonas syringae Lz4W lacking RNase R.J Biol Chem. 2024 Aug;300(8):107600. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107600. Epub 2024 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39059490 Free PMC article.
-
Exoribonuclease R in Pseudomonas syringae is essential for growth at low temperature and plays a novel role in the 3' end processing of 16 and 5 S ribosomal RNA.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jun 1;282(22):16267-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605588200. Epub 2007 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17405875
-
rnr gene from the antarctic bacterium Pseudomonas syringae Lz4W, encoding a psychrophilic RNase R.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Nov;77(22):7896-904. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05683-11. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21926201 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into the ecology of a psychrotolerant Pseudomonas syringae.Environ Microbiol. 2021 Jul;23(7):3665-3681. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15304. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33169927 Review.
-
RNase II: the finer details of the Modus operandi of a molecular killer.RNA Biol. 2010 May-Jun;7(3):276-81. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.3.11490. Epub 2010 May 9. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 20484980 Review.
Cited by
-
A type II toxin-antitoxin system is responsible for the cell death at low temperature in Pseudomonas syringae Lz4W lacking RNase R.J Biol Chem. 2024 Aug;300(8):107600. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107600. Epub 2024 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39059490 Free PMC article.
-
RNase R vs. PNPase: selecting the best-suited exoribonuclease for environmental adaptation.Extremophiles. 2024 Jul 25;28(3):35. doi: 10.1007/s00792-024-01350-6. Extremophiles. 2024. PMID: 39052080 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
