TERRA R-loops connect and protect sister telomeres in mitosis
- PMID: 37843976
- PMCID: PMC10873023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113235
TERRA R-loops connect and protect sister telomeres in mitosis
Abstract
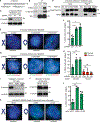
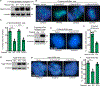
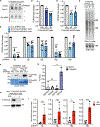
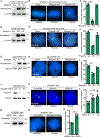
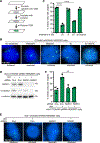
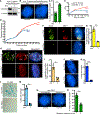
Resolution of cohesion between sister telomeres in human cells depends on TRF1-mediated recruitment of the polyADP-ribosyltransferase tankyrase to telomeres. In human aged cells, due to insufficient recruitment of TRF1/tankyrase to shortened telomeres, sisters remain cohered in mitosis. This persistent cohesion plays a protective role, but the mechanism by which sisters remain cohered is not well understood. Here we show that telomere repeat-containing RNA (TERRA) holds sister telomeres together through RNA-DNA hybrid (R-loop) structures. We show that a tankyrase-interacting partner, the RNA-binding protein C19orf43, is required for repression of TERRA R-loops. Persistent telomere cohesion in C19orf43-depleted cells is counteracted by RNaseH1, confirming that RNA-DNA hybrids hold sisters together. Consistent with a protective role for persistent telomere cohesion, depletion of C19orf43 in aged cells reduces DNA damage and delays replicative senescence. We propose that the inherent inability of shortened telomeres to recruit R-loop-repressing machinery permits a controlled onset of senescence.
Keywords: C19orf43; CP: Molecular biology; R-Loops; RNA-DNA hybrids; RNaseH; TERRA; TRF1; cohesion; senescence; tankyrase; telomeres.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests There are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- de Lange T (2005). Shelterin: the protein complex that shapes and sfeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev 19, 2100–2110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

