Development of a one-step reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
- PMID: 37844073
- PMCID: PMC10578580
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293042
Development of a one-step reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
Abstract
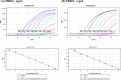
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) caused by PRRS virus (PRRSV) is an important disease that severely affects the swine industry and, therefore, warrants rapid and accurate diagnosis for its control. Despite the progress in developing diagnostic tools, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based methods such as reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) to diagnose PRRSV infection, its diagnosis at the genetic level is challenging because of its high genetic variability. Nevertheless, RT-qPCR is the easiest and fastest method for diagnosing PRRSV. Therefore, this study aimed to develop an RT-qPCR assay for rapid and accurate diagnosis of PRRSV by encompassing all publicly available PRRSV sequences. The developed assay using highly specific primers and probes could detect up to 10 copies of PRRSV-1 and -2 subtypes. Furthermore, a comparison of the performance of the developed assay with those of two commercial kits widely used in South Korea demonstrated the higher efficiency of the developed assay in detecting PRRSV infections in field samples. For PRRSV-1 detection, the developed assay showed a diagnostic agreement of 97.7% with the results of ORF5 sequencing, while for commercial kits, it showed 95.3% and 72.1% agreement. For PRRSV-2, the developed assay showed a diagnostic agreement of 97.7%, whereas the commercial kits showed 93% and 90.7% agreement. In conclusion, we developed an assay with higher accuracy than those of the tested commercial kits, which will contribute markedly to global PRRSV control.
Copyright: © 2023 Chae et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang YT, Guo XQ, Callahan JD, Yuan GL, Zhang GH, Chen Y, et al. Field evaluation of two commercial RT-rtPCR assays for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus detection using sera from ill and healthy pigs, China. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2018;30(6):848–54. doi: 10.1177/1040638718800357 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

