Signal transduction at GPCRs: Allosteric activation of the ERK MAPK by β-arrestin
- PMID: 37844230
- PMCID: PMC10614829
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2303794120
Signal transduction at GPCRs: Allosteric activation of the ERK MAPK by β-arrestin
Abstract
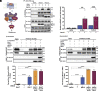
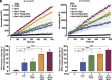
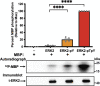
β-arrestins are multivalent adaptor proteins that bind active phosphorylated G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to inhibit G protein signaling, mediate receptor internalization, and initiate alternative signaling events. β-arrestins link agonist-stimulated GPCRs to downstream signaling partners, such as the c-Raf-MEK1-ERK1/2 cascade leading to ERK1/2 activation. β-arrestins have been thought to transduce signals solely via passive scaffolding by facilitating the assembly of multiprotein signaling complexes. Recently, however, β-arrestin 1 and 2 were shown to activate two downstream signaling effectors, c-Src and c-Raf, allosterically. Over the last two decades, ERK1/2 have been the most intensely studied signaling proteins scaffolded by β-arrestins. Here, we demonstrate that β-arrestins play an active role in allosterically modulating ERK kinase activity in vitro and within intact cells. Specifically, we show that β-arrestins and their GPCR-mediated active states allosterically enhance ERK2 autophosphorylation and phosphorylation of a downstream ERK2 substrate, and we elucidate the mechanism by which β-arrestins do so. Furthermore, we find that allosteric stimulation of dually phosphorylated ERK2 by active-state β-arrestin 2 is more robust than by active-state β-arrestin 1, highlighting differential capacities of β-arrestin isoforms to regulate effector signaling pathways downstream of GPCRs. In summary, our study provides strong evidence for a new paradigm in which β-arrestins function as active "catalytic" scaffolds to allosterically unlock the enzymatic activity of signaling components downstream of GPCR activation.
Keywords: ERK MAPK; catalytic scaffolds; scaffold proteins; signal transduction; β-arrestin.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J.L. is a founder of Trevena, Inc. and Septerna, Inc., companies that discover and develop novel GPCR-targeted therapeutics. R.J.L. is also on the board of Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. S.A. is a shareholder of Septerna. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Lefkowitz R. J., A brief history of G-protein coupled receptors (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 52, 6366–6378 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Pierce K. L., Premont R. T., Lefkowitz R. J., Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 3, 639–650 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Beta-arrestin: A protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science 248, 1547–1550 (1990). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

