Mitochondrial transplantation attenuates traumatic neuropathic pain, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis in rats with nerve root ligation
- PMID: 37845039
- PMCID: PMC10605811
- DOI: 10.1177/17448069231210423
Mitochondrial transplantation attenuates traumatic neuropathic pain, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis in rats with nerve root ligation
Abstract
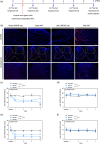
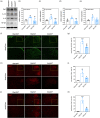
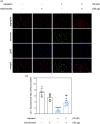
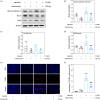
Traumatic neuropathic pain (TNP) is caused by traumatic damage to the somatosensory system and induces the presentation of allodynia and hyperalgesia. Mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis are hallmarks in the pathogenesis of TNP. Recently, mitochondria-based therapy has emerged as a potential therapeutic intervention for diseases related to mitochondrial dysfunction. However, the therapeutic effectiveness of mitochondrial transplantation (MT) on TNP has rarely been investigated. Here, we validated the efficacy of MT in treating TNP. Both in vivo and in vitro TNP models by conducting an L5 spinal nerve ligation in rats and exposing the primary dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons to capsaicin, respectively, were applied in this study. The MT was operated by administrating 100 µg of soleus-derived allogeneic mitochondria into the ipsilateral L5 DRG in vivo and the culture medium in vitro. Results showed that the viable transplanted mitochondria migrated into the rats' spinal cord and sciatic nerve. MT alleviated the nerve ligation-induced mechanical and thermal pain hypersensitivity. The nerve ligation-induced glial activation and the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and apoptotic markers in the spinal cord were also repressed by MT. Consistently, exogenous mitochondria reversed the capsaicin-induced reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential and expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and apoptotic markers in the primary DRG neurons in vitro. Our findings suggest that MT mitigates the spinal nerve ligation-induced apoptosis and neuroinflammation, potentially playing a role in providing neuroprotection against TNP.
Keywords: Apoptosis; mitochondrial dysfunction; mitochondrial transplantation; neuroinflammation; traumatic neuropathic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Ciaramitaro P, Mondelli M, Logullo F, Grimaldi S, Battiston B, Sard A, Scarinzi C, Migliaretti G, Faccani G, Cocito D, Italian Network for Traumatic N. Traumatic peripheral nerve injuries: epidemiological findings, neuropathic pain and quality of life in 158 patients. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2010; 15: 120–127. - PubMed
-
- van Horssen J, van Schaik P, Witte M. Inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction: A vicious circle in neurodegenerative disorders? Neurosci Lett 2019; 710: 132931. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

