Adaptive preservation of orphan ribosomal proteins in chaperone-dispersed condensates
- PMID: 37845327
- PMCID: PMC10868727
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-023-01253-2
Adaptive preservation of orphan ribosomal proteins in chaperone-dispersed condensates
Abstract
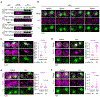
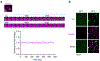
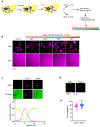
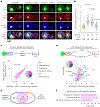
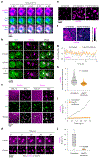
Ribosome biogenesis is among the most resource-intensive cellular processes, with ribosomal proteins accounting for up to half of all newly synthesized proteins in eukaryotic cells. During stress, cells shut down ribosome biogenesis in part by halting rRNA synthesis, potentially leading to massive accumulation of aggregation-prone 'orphan' ribosomal proteins (oRPs). Here we show that, during heat shock in yeast and human cells, oRPs accumulate as reversible peri-nucleolar condensates recognized by the Hsp70 co-chaperone Sis1/DnaJB6. oRP condensates are liquid-like in cell-free lysate but solidify upon depletion of Sis1 or inhibition of Hsp70. When cells recover from heat shock, oRP condensates disperse in a Sis1- and Hsp70-dependent manner, and the oRP constituents are incorporated into functional ribosomes in the cytosol, enabling cells to efficiently resume growth. Preserving biomolecules in reversible condensates-like mRNAs in cytosolic stress granules and oRPs at the nucleolar periphery-may be a primary function of the Hsp70 chaperone system.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
We declare that none of the authors has competing financial or non-financial interests.
Figures



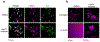







Similar articles
-
The Heat Shock Response as a Condensate Cascade.J Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 15;436(14):168642. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168642. Epub 2024 Jun 5. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38848866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A ribosome-anchored chaperone network that facilitates eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2010 Apr 5;189(1):69-81. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201001054. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20368619 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperones directly and efficiently disperse stress-triggered biomolecular condensates.Mol Cell. 2022 Feb 17;82(4):741-755.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.01.005. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35148816 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of Ydj1 and Sis1 on Hsp70-mediated clearance of stress granules in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.RNA. 2015 Sep;21(9):1660-71. doi: 10.1261/rna.053116.115. Epub 2015 Jul 21. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26199455 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of chaperones on yeast prions: CURrent view.Curr Genet. 2018 Apr;64(2):317-325. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0750-3. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28932898 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective Translation Under Heat Shock: Integrating HSP70 mRNA Regulation with Cellular Stress Responses in Yeast and Mammals.Mol Biol Cell. 2025 May 1;36(5):re2. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-12-0564. Mol Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 40198146 Review.
-
The Heat Shock Response as a Condensate Cascade.J Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 15;436(14):168642. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168642. Epub 2024 Jun 5. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38848866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear and cytosolic J-domain proteins provide synergistic control of Hsf1 at distinct phases of the heat shock response.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 8:2025.04.14.648540. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.14.648540. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40672285 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Heat Shock Factor 1 forms nuclear condensates and restructures the yeast genome before activating target genes.Elife. 2024 Oct 15;12:RP92464. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92464. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39405097 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback control of the heat shock response by spatiotemporal regulation of Hsp70.J Cell Biol. 2024 Dec 2;223(12):e202401082. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202401082. Epub 2024 Sep 20. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39302312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warner JR The economics of ribosome biosynthesis in yeast. Trends Biochem. Sci 24, 437–440 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Maaløe O & Kjeldgaard NO Control of macromolecular synthesis; a study of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in bacteria. (W. A. Benjamin, 1966).
-
- Lempiainen H & Shore D Growth control and ribosome biogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 21, 855–863 (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

