Global Barriers to Accessing Off-Patent Endocrine Therapies: A Renaissance of the Orphan Disease?
- PMID: 37846800
- PMCID: PMC11031238
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgad610
Global Barriers to Accessing Off-Patent Endocrine Therapies: A Renaissance of the Orphan Disease?
Abstract
Context: Clinical endocrinology encompasses many diseases requiring long-term drug therapy. Prohibitive pricing of some endocrine drugs classified as essential by the World Health Organization has created suboptimal care of patients with endocrine disorders.
Evidence acquisition: This review is based on evidence obtained from several databases and search engines including PubMed, Google, and Google Scholar; reference searches; manual searching for web pages of international regulatory bodies; and the authors' experience from different healthcare settings.
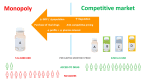
Evidence synthesis: After the expiry of a patent, generic versions with the opportunity for increased availability and a price reduction are expected. There are access barriers worldwide for many off-patent endocrine drugs. The high price is the main issue for several medicines including insulin, hydrocortisone, testosterone, and gonadotropins. This is caused by several factors including the market monopoly due to the lack of registered generics or suppliers limiting the benefit of competition and a complex supply chain. Additionally, the lack of some medicines has been concerning due to market factors such as the relatively small number of patients, making it less attractive for the manufacturers. Commissioning of nonprofit manufacturers and state manufacturing as well as strict price control measures could alleviate this situation.
Conclusion: Lack of availability and disproportionate price inflation affecting essential off-patent endocrine therapies is common due to several interrelated factors. Global collaboration among healthcare organizations with the support of policymaking bodies might be needed to mitigate this.
Keywords: access; availability; cost; endocrine; medicines; off-patent.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Bhutta ZA, Salam RA, Gomber A, et al. A century past the discovery of insulin: global progress and challenges for type 1 diabetes among children and adolescents in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2021;398(10313):1837‐1850. - PubMed
-
- Meeran K, Choudhury SM, Wass J. The scandal of generic drug pricing: drug regulation policies need review. BMJ. 2017;356:j947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

