Single-cell landscape and spatial transcriptomic analysis reveals macrophage infiltration and glycolytic metabolism in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- PMID: 37847178
- PMCID: PMC10637799
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205128
Single-cell landscape and spatial transcriptomic analysis reveals macrophage infiltration and glycolytic metabolism in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
Abstract
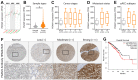
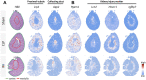
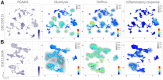
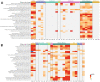
The present study investigates the clinical relevance of glycolytic factors, specifically PGAM1, in the tumor microenvironment of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC). Despite the established role of glycolytic metabolism in cancer pathophysiology, the prognostic implications and key targets in KIRC remain elusive. We analyzed GEO and TCGA datasets to identify DEGs in KIRC and studied their relationship with immune gene expression, survival, tumor stage, gene mutations, and infiltrating immune cells. We explored Pgam1 gene expression in different kidney regions using spatial transcriptomics after mouse kidney injury analysis. Single-cell RNA-sequencing was used to assess the association of PGAM1 with immune cells. Findings were validated with tumor specimens from 60 KIRC patients, correlating PGAM1 expression with clinicopathological features and prognosis using bioinformatics and immunohistochemistry. We demonstrated the expression of central gene regulators in renal cancer in relation to genetic variants, deletions, and tumor microenvironment. Mutations in these hub genes were positively associated with distinct immune cells in six different immune datasets and played a crucial role in immune cell infiltration in KIRC. Single-cell RNA-sequencing revealed that elevated PGAM1 was associated with immune cell infiltration, specifically macrophages. Furthermore, pharmacogenomic analysis of renal cancer cell lines indicated that inactivation of PGAM1 was associated with increased sensitivity to specific small-molecule drugs. Altered PGAM1 in KIRC is associated with disease progression and immune microenvironment. It has diagnostic and prognostic implications, indicating its potential in precision medicine and drug screening.
Keywords: PGAM1; glycolytic metabolism; immune infiltration; kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; single cell-RNA sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Dissecting order amidst chaos of programmed cell deaths: construction of a diagnostic model for KIRC using transcriptomic information in blood-derived exosomes and single-cell multi-omics data in tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 19;14:1130513. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1130513. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37153569 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling infiltrating T-cell heterogeneity in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma: Integrative single-cell and spatial transcriptomic profiling.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18403. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18403. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39031800 Free PMC article.
-
Supervised Learning and Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Clinical Significance of Inner Membrane Mitochondrial Protein (IMMT) in Prognostic Prediction, Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Precision Medicine for Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 15;24(10):8807. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108807. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240154 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of a novel signature based on macrophage marker genes for predicting prognosis and drug response in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma by integrated analysis of single cell and bulk RNA sequencing.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 20;16(6):5676-5702. doi: 10.18632/aging.205671. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38517387 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic signature of chemokines for survival and immune infiltration in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Jun 19;20(8):1046-1059. doi: 10.7150/ijms.84940. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37484803 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatics screening of prognostic immune-related genes in renal clear cell carcinoma.J Appl Genet. 2025 May;66(2):311-322. doi: 10.1007/s13353-024-00878-9. Epub 2024 May 23. J Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 38780866
-
Spatial Transcriptomics: A Powerful Tool in Disease Understanding and Drug Discovery.Theranostics. 2024 May 11;14(7):2946-2968. doi: 10.7150/thno.95908. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38773973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A phosphoglycerate mutase 1 allosteric inhibitor restrains TAM-mediated colon cancer progression.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Nov;14(11):4819-4831. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.09.007. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39664444 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omics Reveals the Role of Osteopontin/Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 in Regulating Ovarian Aging.J Pers Med. 2024 Jan 9;14(1):78. doi: 10.3390/jpm14010078. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38248779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Linehan WM, Vasselli J, Srinivasan R, Walther MM, Merino M, Choyke P, Vocke C, Schmidt L, Isaacs JS, Glenn G, Toro J, Zbar B, Bottaro D, Neckers L. Genetic basis of cancer of the kidney: disease-specific approaches to therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:6282S–9S. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-050013 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

