Granuloma, vasculitis, and demyelination in sarcoid neuropathy
- PMID: 37847215
- PMCID: PMC11235865
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.16091
Granuloma, vasculitis, and demyelination in sarcoid neuropathy
Abstract
Background: Despite the suggestion that direct compression by granuloma and ischemia resulting from vasculitis can cause nerve fiber damage, the mechanisms underlying sarcoid neuropathy have not yet been fully clarified.
Methods: We examined the clinicopathological features of sarcoid neuropathy by focusing on electrophysiological and histopathological findings of sural nerve biopsy specimens. We included 18 patients with sarcoid neuropathy who had non-caseating epithelioid cell granuloma in their sural nerve biopsy specimens.
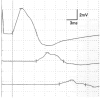
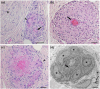
Results: Although electrophysiological findings suggestive of axonal neuropathy were observed, particularly in the lower limbs, all but three patients showed ≥1 abnormalities in nerve conduction velocity or distal motor latency. Additionally, a conduction block was observed in 11 of the 16 patients for whom waveforms were assessed; five of them fulfilled motor nerve conduction criteria strongly supportive of demyelination as defined in the European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society (EAN/PNS) guideline for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). In most patients, sural nerve biopsy specimens revealed a mild to moderate degree of myelinated fiber loss. Fibrinoid necrosis was observed in one patient, and electron microscopy analysis revealed demyelinated axons close to granulomas in six patients.
Conclusions: Patients with sarcoid neuropathy may meet the EAN/PNS electrophysiological criteria for CIDP due to the frequent presence of conduction blocks. Based on our results, in addition to the ischemic damage resulting from granulomatous inflammation, demyelination may play an important role in the mechanism underlying sarcoid neuropathy.
Keywords: conduction block; demyelination; electrophysiology; granuloma; pathology; sarcoid neuropathy.
© 2023 The Authors. European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nerve granulomas and vasculitis in sarcoid peripheral neuropathy: a clinicopathological study of 11 patients.Brain. 2002 Feb;125(Pt 2):264-75. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf027. Brain. 2002. PMID: 11844727
-
Two distinct mechanisms of neuropathy in immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis.J Neurol Sci. 2021 Feb 15;421:117305. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.117305. Epub 2021 Jan 2. J Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33540321
-
Focal Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy - A Case Report with Clinical Application and Validation of 2021 European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society Criteria.Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2025 Jan 1;34(1):24-27. doi: 10.4103/ANT.ANT_112_0101. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2025. PMID: 40396798
-
[Physiological approach to peripheral neuropathy. Conventional nerve conduction studies and magnetic motor root stimulation].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2004 Nov;44(11):986-90. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2004. PMID: 15651350 Review. Japanese.
-
[Histopathological features of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2006 Apr;162(4):527-32. doi: 10.1016/s0035-3787(06)75046-9. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2006. PMID: 16585916 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Electrophysiological Characteristics of 23 French Patients With Neurolymphomatosis.Muscle Nerve. 2025 Apr;71(4):535-542. doi: 10.1002/mus.28343. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Muscle Nerve. 2025. PMID: 39777678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siltzbach LE, James DG, Neville E, et al. Course and prognosis of sarcoidosis around the world. Am J Med. 1974;57(6):847‐852. - PubMed
-
- Stern BJ, Krumholz A, Johns C, Scott P, Nissim J. Sarcoidosis and its neurological manifestations. Arch Neurol. 1985;42(9):909‐917. - PubMed
-
- Burns TM. Neurosarcoidosis. Arch Neurol. 2003;60(8):1166‐1168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

