A randomized, double-blind study on the efficacy of oral domperidone versus placebo for reducing SARS-CoV-2 viral load in mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients in primary health care
- PMID: 37847999
- PMCID: PMC10583612
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2268535
A randomized, double-blind study on the efficacy of oral domperidone versus placebo for reducing SARS-CoV-2 viral load in mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients in primary health care
Abstract
Introduction: The clinical effect of domperidone against COVID-19 has been investigated in a double-blind phase III clinical trial (EudraCT number 2021-001228-17). Domperidone has shown in vitro antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and potential immudolatory properties through the stimulation of prolactin secretion.
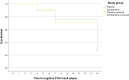
Patients and methods: The efficacy of oral domperidone plus standard of care (SOC; n = 87) versus placebo plus SOC (n = 86) was evaluated in a 28-day randomized double-blind multicentre study in primary health care centres. A total of 173 outpatients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 were included. Three daily doses of 10 mg (30 mg/day) of domperidone or placebo were administered for 7 days. Reduction of viral load on day 4 was the primary efficay endpoint. It was estimated in saliva samples by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), as the cycle thresholds detected ORF1ab, N Protein and S Protein genes.
Results: A significant reduction in the viral load was observed (p < 0.001) from baseline to days 4, 7 and 14 of the three genes studied with non-significant differences between domperidone and placebo groups. Twenty-three patients (13.3%) experienced adverse events, 14 patients in the domperidone group (16.1%) and 9 patients in the placebo group (10.5%). No patients needed to be hospitalized.
Conclusion: Results do not prove the use of domperidone as antiviral in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19 disease; PCR; SARS-CoV-2 virus; domperidone.
Plain language summary
A 28-day double-blind clinical trial was performed to investigate the antiviral effect of domperidone, 30 mg/day for 7 days (n = 87) versus placebo (n = 86) in outpatients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19.The primary efficacy endpoint was the reduction of viral load on day 4 as compared with baseline, estimated as the cycle thresholds to detect ORF1ab, N Protein and S Protein genes by RT-qPCR in saliva samples.The study findings do not prove the use of domperidone as antiviral in patients with COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Martínez and C. Gil are employees of the sponsor Agencia Estatal Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, M.P. (CSIC). B. Soler López was contracted to carry out the design, monitoring, statistical analysis and management of the publications derived from the study. The other authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Martinez A, Gil C, Gastaminza P, et al. Domperidone for use as antiviral agent. EP3949965, WO2022028839, priority date 07/08/2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous