Material-agnostic machine learning approach enables high relative density in powder bed fusion products
- PMID: 37848436
- PMCID: PMC10582079
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42319-x
Material-agnostic machine learning approach enables high relative density in powder bed fusion products
Abstract
This study introduces a method that is applicable across various powder materials to predict process conditions that yield a product with a relative density greater than 98% by laser powder bed fusion. We develop an XGBoost model using a dataset comprising material properties of powder and process conditions, and its output, relative density, undergoes a transformation using a sigmoid function to increase accuracy. We deeply examine the relationships between input features and the target value using Shapley additive explanations. Experimental validation with stainless steel 316 L, AlSi10Mg, and Fe60Co15Ni15Cr10 medium entropy alloy powders verifies the method's reproducibility and transferability. This research contributes to laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing by offering a universally applicable strategy to optimize process conditions.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

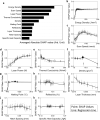
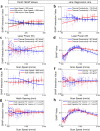

References
-
- Bibb, R. Physical reproduction – rapid prototyping technologies. Med. Model10.1533/9781845692001.59 (2006).
-
- Ahmed N, Barsoum I, Haidemenopoulos G, Al-Rub RKA. Process parameter selection and optimization of laser powder bed fusion for 316L stainless steel: a review. J. Manuf. Process. 2022;75:415–434.
-
- Al-Maharma AY, Patil SP, Markert B. Effects of porosity on the mechanical properties of additively manufactured components: a critical review. Mater. Res. Express. 2020;7:122001.
-
- Olakanmi EO, Cochrane RF, Dalgarno KW. Densification mechanism and microstructural evolution in selective laser sintering of Al–12Si powders. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011;211:113–121.
-
- Prashanth KG, Scudino S, Maity T, Das J, Eckert J. Is the energy density a reliable parameter for materials synthesis by selective laser melting? Mater. Res. Lett. 2017;5:386–390.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

