Unlocking potential inhibitors for Bruton's tyrosine kinase through in-silico drug repurposing strategies
- PMID: 37848584
- PMCID: PMC10582150
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-44956-0
Unlocking potential inhibitors for Bruton's tyrosine kinase through in-silico drug repurposing strategies
Abstract
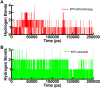
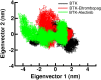
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor protein kinase that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including immune system function and cancer development. Therefore, inhibition of BTK has been proposed as a therapeutic strategy for various complex diseases. In this study, we aimed to identify potential inhibitors of BTK by using a drug repurposing approach. To identify potential inhibitors, we performed a molecular docking-based virtual screening using a library of repurposed drugs from DrugBank. We then used various filtrations followed by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, principal component analysis (PCA), and Molecular Mechanics Poisson Boltzmann Surface Area (MM-PBSA) analysis to further evaluate the binding interactions and stability of the top-ranking compounds. Molecular docking-based virtual screening approach identified several repurposed drugs as potential BTK inhibitors, including Eltrombopag and Alectinib, which have already been approved for human use. All-atom MD simulations provided insights into the binding interactions and stability of the identified compounds, which will be helpful for further experimental validation and optimization. Overall, our study demonstrates that drug repurposing is a promising approach to identify potential inhibitors of BTK and highlights the importance of computational methods in drug discovery.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

