Combined telemonitoring and telecoaching for heart failure improves outcome
- PMID: 37848681
- PMCID: PMC10582035
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-023-00942-4
Combined telemonitoring and telecoaching for heart failure improves outcome
Abstract
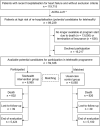
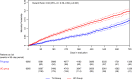
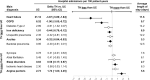
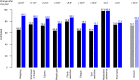
Telemedicine has been shown to improve the outcome of heart failure (HF) patients in addition to medical and device therapy. We investigate the effectiveness of a comprehensive telehealth programme in patients with recent hospitalisation for HF on subsequent HF hospitalisations and mortality compared to usual care in a real-world setting. The telehealth programme consists of daily remote telemonitoring of HF signs/symptoms and regular individualised telecoaching sessions. Between January 2018 and September 2020, 119,715 patients of a German health insurer were hospitalised for HF and were eligible for participation in the programme. Finally, 6065 HF patients at high risk for re-hospitalisation were enroled. Participants were retrospectively compared to a propensity score matched usual care group (n = 6065). Median follow-up was 442 days (IQR 309-681). Data from the health insurer was used to evaluate outcomes. After one year, the number of hospitalisations for HF (17.9 vs. 21.8 per 100 patient years, p < 0.001), all-cause hospitalisations (129.0 vs. 133.2 per 100 patient years, p = 0.015), and the respective days spent in hospital (2.0 vs. 2.6 days per year, p < 0.001, and 12.0 vs. 13.4, p < 0.001, respectively) were significantly lower in the telehealth than in the usual care group. Moreover, participation in the telehealth programme was related to a significant reduction in all-cause mortality compared to usual care (5.8 vs. 11.0 %, p < 0.001). In a real-life setting of ambulatory HF patients at high risk for re-hospitalisation, participation in a comprehensive telehealth programme was related to a reduction of HF hospitalisations and all-cause mortality compared to usual care.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
C.K. was managing director of HCSG, D.D. is employee of HCSG. S.Sc. is employee of Krankenkasse Knappschaft. S.Sa. and C.H are employees of Novartis Pharma GmbH. K.K., S.R., S.G., T.T., C.L., M.D., H.S., and W.R. declare that they have no conflict of interest in regard to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Koehler F, et al. Telemedical Interventional Management in Heart Failure II (TIM-HF2), a randomised, controlled trial investigating the impact of telemedicine on unplanned cardiovascular hospitalisations and mortality in heart failure patients: study design and description of the intervention. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018;20:1485–1493. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1300. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

