A research synthesis on successful educational practices and student outcomes for physical education in schools
- PMID: 37849483
- PMCID: PMC10577211
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1280871
A research synthesis on successful educational practices and student outcomes for physical education in schools
Abstract
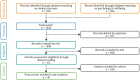
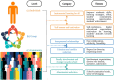
Although successful educational practices (SEPs) in higher education institutions have well-established student outcomes, the vast majority do not meet physical education standards in schools. Despite the promising nature of policy initiatives supporting schools, there is scant evidence of how these SEPs affect student outcomes. This review aimed to determine the status of the literature and the type of evidence regarding school SEPs. Several studies have demonstrated that these SEPs contribute directly or indirectly to improving student outcomes. Three objectives were examined and synthesized in our review of SEP research findings. The first goal is to identify different types of impacts on students in schools. The second goal is to provide educators, principals, and policymakers with a unified and comprehensive framework. Lastly, we provide suggestions for future SEP research. The review identified 45 studies that met our inclusion criteria. Our reviewed studies documented impacts on the individual level. It encompasses both students' instrumental abilities and their sense of self-esteem and motivation. Secondly, improving interpersonal relationships, reducing conflict, and increasing group cohesion are important components at the group level. Finally, there are factors at the community level, including absenteeism reduction, parental involvement, and changes in attitudes toward school. Current research supports the effectiveness of successful school practices. It stresses the importance of implementing policies to maximize student outcomes. Finally, the review concludes by discussing findings implications and future research directions.
Keywords: educational interventions; physical activity; policy; professional development; school education; student performance.
Copyright © 2023 He, Yu, Jiang and Bialas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arif M., Jiajia L., Tahir M., Jie Z., Li C. (2023). Environmental literacy scenarios lead to land degradation and changes in riparian zones: implications for policy in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 34, 156–172. 10.1002/ldr.4450 - DOI
-
- Aubert A. (2015). Amaya: Dialogic literary gatherings evoking passion for learning and a transformation of the relationships of a Roma girl with her classmates. Qual. Inq. 21, 858–864. 10.1177/1077800415614034 - DOI
-
- Aubert A., Molina S., Schubert T., Vidu A. (2017). Learning and inclusivity via interactive groups in early childhood education and care in the hope school, Spain. Learn. Cult. Soc. Interact. 13, 90–103. 10.1016/j.lcsi.2017.03.002 - DOI
-
- Bakir Y., Kangalgil M. J. J. o,.E, Studies T. (2017). The effect of sport on the level of positivity and well-being in adolescents engaged in sport regularly. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 5, 98–104. 10.11114/jets.v5i11.2592 - DOI
-
- Beaulac J., Kristjansson E., Calhoun M. (2011). 'Bigger than hip-hop?' Impact of a community-based physical activity program on youth living in a disadvantaged neighborhood in Canada. J. Youth Stud. 14, 961–974. 10.1080/13676261.2011.616488 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous