Inhaled nitric oxide: can it serve as a savior for COVID-19 and related respiratory and cardiovascular diseases?
- PMID: 37849924
- PMCID: PMC10577426
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277552
Inhaled nitric oxide: can it serve as a savior for COVID-19 and related respiratory and cardiovascular diseases?
Abstract
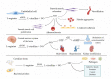
Nitric oxide (NO), as an important gaseous medium, plays a pivotal role in the human body, such as maintaining vascular homeostasis, regulating immune-inflammatory responses, inhibiting platelet aggregation, and inhibiting leukocyte adhesion. In recent years, the rapid prevalence of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has greatly affected the daily lives and physical and mental health of people all over the world, and the therapeutic efficacy and resuscitation strategies for critically ill patients need to be further improved and perfected. Inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) is a selective pulmonary vasodilator, and some studies have demonstrated its potential therapeutic use for COVID-19, severe respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary infections, and pulmonary hypertension. In this article, we describe the biochemistry and basic characteristics of NO and discuss whether iNO can act as a "savior" for COVID-19 and related respiratory and cardiovascular disorders to exert a potent clinical protective effect.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute respiratory distress syndrome; inhaled nitric oxide; lung infection; nitric oxide; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Li, Zhang, Cheng, Liu, Han, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Afshari A., Brok J., Møller A. M., Wetterslev J. (2011). Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury in adults and children: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Anesth. Analg. 112, 1411–1421. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31820bd185 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al Sulaiman K., Korayem G. B., Altebainawi A. F., Al Harbi S., Alissa A., Alharthi A., et al. . (2022). Evaluation of inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) treatment for moderate-to-severe ARDS in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study. Crit. Care 26:304. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04158-y, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

