Genomic analysis of the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) and the cynomolgus macaque (Macaca fascicularis) uncover polygenic signatures of reinforcement speciation
- PMID: 37849934
- PMCID: PMC10577069
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.10571
Genomic analysis of the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) and the cynomolgus macaque (Macaca fascicularis) uncover polygenic signatures of reinforcement speciation
Abstract
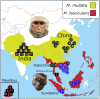
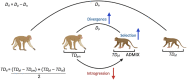
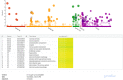
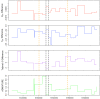
Speciation can involve phases of divergent adaptation in allopatry and ecological/reproductive character displacement in sympatry or parapatry. Reproductive character displacement can result as a means of preventing hybridization, a process known as reinforcement speciation. In this study, we use whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of two closely related primate species that have experienced introgression in their history, the rhesus (Macaca mulatta) and cynomolgus (M. fascicularis) macaques, to identify genes exhibiting reproductive character displacement and other patterns consistent with reinforcement speciation. Using windowed scans of various population genetic statistics to identify signatures of reinforcement, we find 184 candidate genes associated with a variety of functions, including an overrepresentation of multiple neurological functions and several genes involved in sexual development and gametogenesis. These results are consistent with a variety of genes acting in a reinforcement process between these species. We also find signatures of introgression of the Y-chromosome that confirm previous studies suggesting male-driven introgression of M. mulatta into M. fascicularis populations. This study uses WGS to find evidence of the process of reinforcement in primates that have medical and conservation relevance.
Keywords: genomics; macaques; reinforcement; speciation.
© 2023 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Andrews, S. (2010). FastQC: A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data (0.10.1).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

