Effects of traditional Chinese exercises on cardiac rehabilitation in patients with myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 37849938
- PMCID: PMC10577298
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1223677
Effects of traditional Chinese exercises on cardiac rehabilitation in patients with myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: Traditional Chinese exercises (TCE) are excellent cardiac rehabilitation (CR) training that can effectively improve cardiorespiratory fitness. However, there is no published meta-analysis of TCE on CR in patients with myocardial infarction (MI). Therefore, this study aimed to provide a comprehensive evaluation from multiple perspectives.
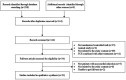
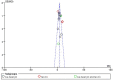
Methods: This meta-analysis is based on the Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews. Eight databases were searched from the date of database construction to March 15, 2023. Two investigators independently screened the literature and assessed their quality. The meta-analysis was performed with RevMan5.4 software.
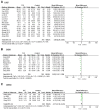
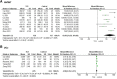
Results: A total of 21 articles involving 1,890 patients were included. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in the TCE group were lower than the control group (MD = -96.34, 95%CI: -140.69 ∼-51.98, P < 0.00001, I2 = 96%), the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in the TCE group was higher than the control group (MD = 4.58, 95%CI: 3.28-5.88, P < 0.00001, I2 = 79%), the left ventricular end diastolic dimension (LVDD) in TCE group was lower than the control group (MD = -3.83, 95%CI: -5.27 ∼-2.38, P < 0.00001, I2 = 94%), the left ventricular end systolic diameter (LVESD) in TCE group was lower than the control group (MD = -2.17, 95%CI: -4.10 ∼-0.24, P < 0.00001, I2 = 96%), The 6-minute walk test (6MWT) in the TCE group was higher than the control group (MD = 69.60, 95%CI: 34.59-104.60, P < 0.00001, I2 = 99%), the oxygen uptake (VO2) in the TCE group was higher than the control group (MD = 4.38, 95%CI: 2.25-6.51, P < 0.00001, I2 = 94%), the 36-item short form survey (SF-36) in the TCE group was higher than the control group (MD = 13.34, 95%CI: 9.25-17.42, P = 0.008, I2 = 75%), the Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA) in the TCE group was lower than the control group (MD = -4.34, 95%CI: -5.18 ∼-3.50, P = 1.00, I2 = 0%), the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD) in the TCE group was lower than the control group (MD = -3.48, 95%CI: -5.35 ∼-1.61, P = 0.0002, I2 = 88%), the incidence of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) in the TCE group was lower than the control group (RR = 0.31, 95%CI: 0.20-0.47, P = 0.52, I2 = 0%). Subgroup analysis revealed differences in TCE types could be a potential source of heterogeneity.
Conclusion: MI patients who used TCE have not only notable improvements in cardiopulmonary function, physical function, quality of life, and emotions but also reduced the incidence of MACEs. Tai Chi might be more efficient than Ba Duan Jin.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42023408675.
Keywords: ba duan jin; cardiac rehabilitation; meta-analysis; myocardial infarction; tai chi; traditional Chinese exercise.
© 2023 Zhang, Weng, Yuan, Shen, Weng and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effect of Ba Duan Jin exercise intervention on cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 6;12:1425843. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1425843. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39165777 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Cardiac Rehabilitation Training in Patients with Heart Failure Based on Traditional Chinese Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Nov 15;2021:1068623. doi: 10.1155/2021/1068623. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34819979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Astragalus membranaceus on left ventricular remodeling in HFrEF: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 12;15:1345797. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1345797. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38283626 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Traditional Chinese Exercises on Patients with Chronic Heart Failure (TCE-HF): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 9;12(6):2150. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062150. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36983152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of Dengzhan Shengmai capsule in the treatment of chronic heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Feb 21;12:1385061. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1385061. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40060965 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Cardioprotective Mechanisms of Ligusticum wallichii in Myocardial Infarction Through Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 17;19:281-302. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S481499. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39845152 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Effectiveness of Multimodal Exercise Combined With Supportive Music and Imagery in the Management of Poststroke Mood Disorders.J Neurosci Nurs. 2025 Apr 1;57(2):61-67. doi: 10.1097/JNN.0000000000000798. Epub 2024 Nov 28. J Neurosci Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39514851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Writing of Committee Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China. Interpretation of report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2021. Chin J Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 27(04):305–18. 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0506 - DOI
-
- Servey JT, Stephens MB. Cardiac rehabilitation: improving function and reducing risk. Am Fam Physician. (2016) 94(1):37–43. - PubMed
-
- Li RJ, Chen HW, Feng JH, Xiao Y, Zhang HY, Lam CWK, et al. Effectiveness of traditional Chinese exercise for symptoms of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17(21):7873. 10.3390/ijerph17217873 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

