Oncoplastic Breast Reduction: A Systematic Review of Postoperative Complications
- PMID: 37850204
- PMCID: PMC10578759
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005355
Oncoplastic Breast Reduction: A Systematic Review of Postoperative Complications
Abstract
Background: Breast-conserving therapy with oncoplastic reduction is a useful strategy for partial mastectomy defect reconstruction. The most recently published systematic review of oncoplastic breast reduction outcomes from 2015 showed wound dehiscence in 4.3%, hematoma in 0.9%, infection in 2.8%, and nipple necrosis in 0.9% of patients. We performed a systematic review of oncoplastic breast reduction literature, comparing outcomes and complication rates reported over the past 8 years.
Methods: Studies describing the use of oncoplastic breast reduction and discussion of postoperative complications were included. The primary outcome assessed was the postoperative complication rate; secondary outcomes analyzed were rates of margin expansion, completion mastectomy, and delays in adjuvant therapy due to complications.
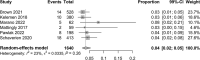
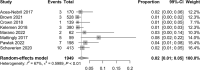
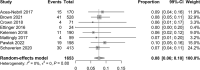
Results: Nine articles met inclusion criteria, resulting in 1715 oncoplastic breast reduction patients. The mean rate of hematoma was 3%, nipple necrosis was 2%, dehiscence was 4%, infection was 3%, and seroma was 2%. The need for re-excision of margins occurred in 8% of patients, and completion mastectomy in 2%. Finally, delay in adjuvant treatment due to a postoperative complication occurred in 4% of patients.
Conclusions: Oncoplastic breast reduction is an excellent option for many patients undergoing breast-conserving therapy; however, postoperative complications can delay adjuvant radiation therapy. Results of this systematic literature review over the past 8 years showed a slight increase in complication rate compared to the most recent systematic review from 2015. With increased popularity and surgeon familiarity, oncoplastic breast reduction remains a viable option for reconstruction of partial mastectomy defects despite a slight increase in complication rate.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article. Disclosure statements are at the end of this article, following the correspondence information.
Figures




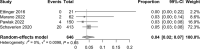
References
-
- Piper ML, Esserman LJ, Sbitany H, et al. . Outcomes following oncoplastic reduction mammoplasty: a systematic review. Ann Plast Surg. 2016;76:S222–S226. - PubMed
-
- Yiannakopoulou EC, Mathelin C. Oncoplastic breast conserving surgery and oncological outcome: systematic review. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016;42:625–630. - PubMed
-
- Bertozzi N, Pesce M, Santi PL, et al. . Oncoplastic breast surgery: comprehensive review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:2572–2585. - PubMed
-
- Nijenhuis MV, Rutgers EJ. Who should not undergo breast conservation? Breast. 2013;22:S110–S114. - PubMed
-
- Chan SW, Cheung PS, Lam SH. Cosmetic outcome and percentage of breast volume excision in oncoplastic breast conserving surgery. World J Surg. 2010;34:1447–1452. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
