Molecular basis of Wnt biogenesis, secretion, and Wnt7-specific signaling
- PMID: 37852257
- PMCID: PMC10841698
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.021
Molecular basis of Wnt biogenesis, secretion, and Wnt7-specific signaling
Abstract
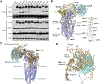
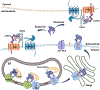
Wnt proteins are enzymatically lipidated by Porcupine (PORCN) in the ER and bind to Wntless (WLS) for intracellular transport and secretion. Mechanisms governing the transfer of these low-solubility Wnts from the ER to the extracellular space remain unclear. Through structural and functional analyses of Wnt7a, a crucial Wnt involved in central nervous system angiogenesis and blood-brain barrier maintenance, we have elucidated the principles of Wnt biogenesis and Wnt7-specific signaling. The Wnt7a-WLS complex binds to calreticulin (CALR), revealing that CALR functions as a chaperone to facilitate Wnt transfer from PORCN to WLS during Wnt biogenesis. Our structures, functional analyses, and molecular dynamics simulations demonstrate that a phospholipid in the core of Wnt-bound WLS regulates the association and dissociation between Wnt and WLS, suggesting a lipid-mediated Wnt secretion mechanism. Finally, the structure of Wnt7a bound to RECK, a cell-surface Wnt7 co-receptor, reveals how RECKCC4 engages the N-terminal domain of Wnt7a to activate Wnt7-specific signaling.
Keywords: N-glycan; Porcupine; RECK; Wnt; Wntless; calreticulin; cryo-EM; phospholipid.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
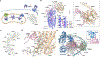

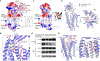
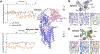

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

