A phase 1a/1b first-in-human study (COMPASSION-01) evaluating cadonilimab in patients with advanced solid tumors
- PMID: 37852261
- PMCID: PMC10694581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101242
A phase 1a/1b first-in-human study (COMPASSION-01) evaluating cadonilimab in patients with advanced solid tumors
Abstract
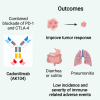
Simultaneous inhibition of programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (CTLA-4) with bispecific antibodies may improve efficacy over single-agent treatment while limiting toxicity. Cadonilimab is a humanized, bispecific antibody targeting PD-1 and CTLA-4. This is a phase 1 study of cadonilimab including dose escalation (n = 39) and dose expansion (n = 80). One dose-limiting toxicity event is observed, with the maximum tolerated dose not reached. 6 mg/kg cadonilimab once every 2 weeks is established as the recommended dose for future studies. The most common treatment-related adverse event is infusion-related reaction (18.5%), mostly grade 1/2 in severity. The incidences of any grade and grade ≥3 immune-related adverse events are 44.5% and 6.7%, respectively. The confirmed overall response rate is 13.4%, and the median duration of response is 12.9 months. Cadonilimab is well tolerated and showed promising efficacy in patients with advanced solid tumors. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03261011.
Keywords: CTLA-4; PD-1; advanced solid tumors; bispecific antibody; cadonilimab; immune checkpoint inhibitor.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.F. has received research funding and honoraria from Amgen; has consulted and advised for Akeso Biopharma and Merck Sharpe and Dohme (MSD); and has received support from Amgen for attending meetings and/or travel and industry trial sponsorship to study site (principal investigator of multiple studies) from Akeso Biopharma, Ambrax, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Aulos, Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), BeiGene, Cullinan, Daiichi Sankyo, Edison Oncology, MSD, Pfizer, Takeda, HaiHe Biopharma, Vivace, and WMS. H.K.G. has consulted/advised for BMS, Curis, Merck Serono, and Telix. B.T. has received research funding from Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Genentech, Ipsen, Janssen, Pfizer, Movember, and MSD; has received honoraria from Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Tolmar; and has served in a consulting/advisory role for Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Ipsen, IQVIA, Janssen, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Tolmar. M.M. has received research funding from BMS and honoraria from BMS, Roche, and the Limbic; has consulted/advised for MSD, the Limbic, Roche, BMS, Takeda, Guardant Health, BeiGene Australia, Amgen, Merck, Lilly, and Novartis; and has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from AstraZeneca. Y.Z., W.W., D.X., M.W., B.L., and M.X. are employees of Akeso Biopharma. J.D. has received institutional research funding from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene,BMS, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche/Genentech, and Eli Lilly and has consulted/advised for Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Lilly, Merck KGaA, Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Antengene, and BeiGene.
Figures


References
-
- Brahmer J.R., Lacchetti C., Schneider B.J., Atkins M.B., Brassil K.J., Caterino J.M., Chau I., Ernstoff M.S., Gardner J.M., Ginex P., et al. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:1714–1768. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Myers Squibb B. 2022. OPDIVO U.S. Prescribing Information.
-
- Myers Squibb B. 2022. YERVOY U.S. Prescribing Information.
-
- Baas P., Scherpereel A., Nowak A.K., Fujimoto N., Peters S., Tsao A.S., Mansfield A.S., Popat S., Jahan T., Antonia S., et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:375–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

