A DEAD-box helicase drives the partitioning of a pro-differentiation NAB protein into nuclear foci
- PMID: 37852948
- PMCID: PMC10584935
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42345-9
A DEAD-box helicase drives the partitioning of a pro-differentiation NAB protein into nuclear foci
Abstract
How cells regulate gene expression in a precise spatiotemporal manner during organismal development is a fundamental question in biology. Although the role of transcriptional condensates in gene regulation has been established, little is known about the function and regulation of these molecular assemblies in the context of animal development and physiology. Here we show that the evolutionarily conserved DEAD-box helicase DDX-23 controls cell fate in Caenorhabditis elegans by binding to and facilitating the condensation of MAB-10, the C. elegans homolog of mammalian NGFI-A-binding (NAB) protein. MAB-10 is a transcriptional cofactor that functions with the early growth response (EGR) protein LIN-29 to regulate the transcription of genes required for exiting the cell cycle, terminal differentiation, and the larval-to-adult transition. We suggest that DEAD-box helicase proteins function more generally during animal development to control the condensation of NAB proteins important in cell identity and that this mechanism is evolutionarily conserved. In mammals, such a mechanism might underlie terminal cell differentiation and when dysregulated might promote cancerous growth.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
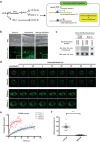
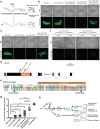
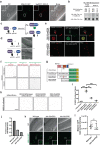
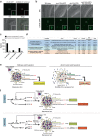
References
-
- Ambros V, Horvitz HR. Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1984;226:409–416. - PubMed
-
- Moss EG. Heterochronic genes and the nature of developmental time. Curr. Biol. 2007;17:R425–R434. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart BJ, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403:901–906. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. A hierarchy of regulatory genes controls a larva-to-adult developmental switch in C. elegans. Cell. 1989;57:49–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

